|
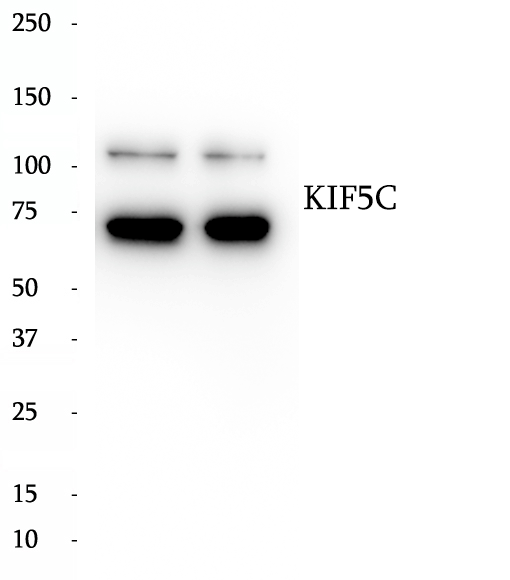
BP62507
|
Anti-KIF5C antibody
|
|
|
|
|
KIF5C (Kinesin heavy chain isoform 5C variant) which belongs to the kinesin-like protein family is neuron specific. The kinesin-1 subfamilies (kif5a, kif5b, kif5c) are responsible for the movement of mitochondria in neurons. Kinesins have N-terminal motor domains and C-terminal cargo-binding tail domains separated by hinge regions. The hinge and C-terminal tail regions of Kif5a, Kif5b, and Kif5c bound a large detergent-resistant RNase-sensitive granule. The granule localized to dendrites and underwent bidirectional movement. Distally directed movement of the granule was enhanced by Kif5 overexpression and reduced by Kif5 functional blockage. kinesins may transport RNA in dendrites via this large granule. Two major isoforms of kif5c, with molecular predicted masses of 80 and 110 kDa, are generated by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP65359
|
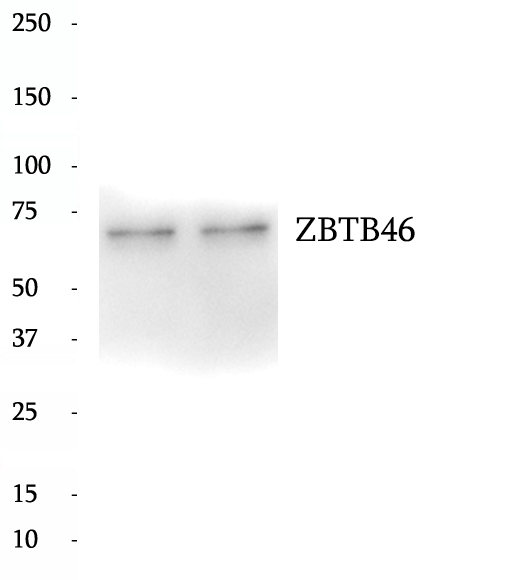
Anti-ZBTB46 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ZBTB46, also named as BTBD4, ZNF340, is a 589 amino acid protein, which contains one BTB (POZ) domain and two C2H2-type zinc fingers. ZBTB46 functions as a transcriptional repressor for PRDM1.
|
|
BP61259
|
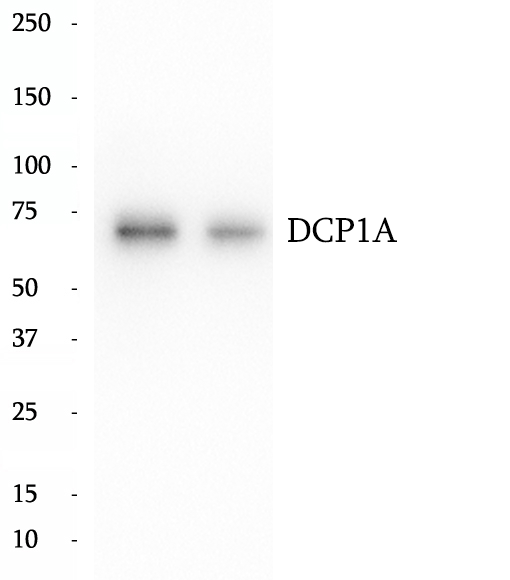
Anti-DCP1A antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DCP1 decapping enzyme homolog A (S. cerevisiae), known as mRNA-decapping enzyme 1A (DCP1A),is necessary for the degradation of mRNAs, both in normal mRNA turnover and in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Removes the 7-methyl guanine cap structure from mRNA molecules, yielding a 5'-phosphorylated mRNA fragment and 7m-GDP. Contributes to the transactivation of target genes after stimulation by TGFB1. This antibody specifically react with the 70kd DCP1A protein.
|
|
BP61374
|
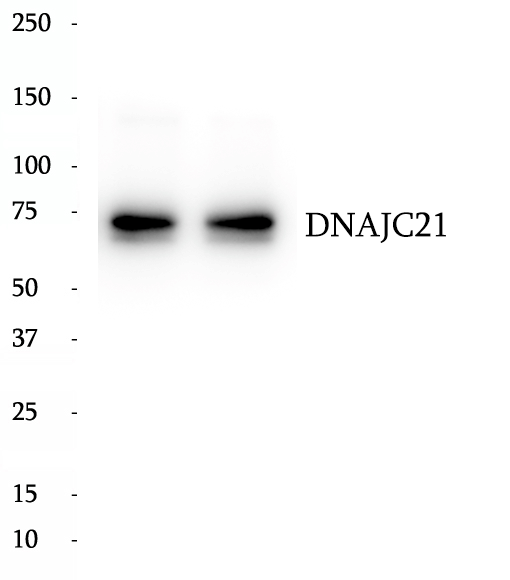
Anti-DNAJC21 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DNAJC21 is a ubiquitously expressed DnaJ (heat shock protein 40) chaperone protein. Recently DNAJC21 was reported to be implicated in rRNA biogenesis. Loss of DNAJC21 induced abnormal cell morphology and inhibited cell growth. Mutations in DNAJC21 cause bone marrow failure syndrome. (27346687)
|
|
BP61431
|
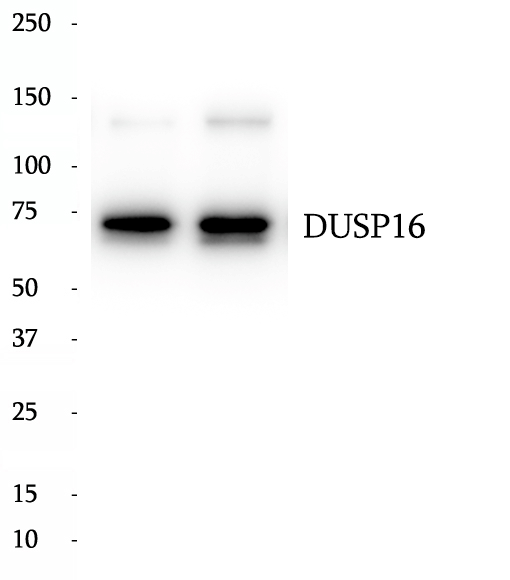
Anti-DUSP16 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DUSP16, also known as MKP-7, is a mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase that is a member of the dual specificity protein phosphatase subfamily. DUSP16 dephosphorylates JUN kinases (JNKs) specifically and thereby regulates T-cell differentiation, which can be responsible for the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma and cerebral ischemia. DUSP16 was also found to induce the expression of VCAM-1 through the suppression of JNK signaling.
|
|
BP65284
|
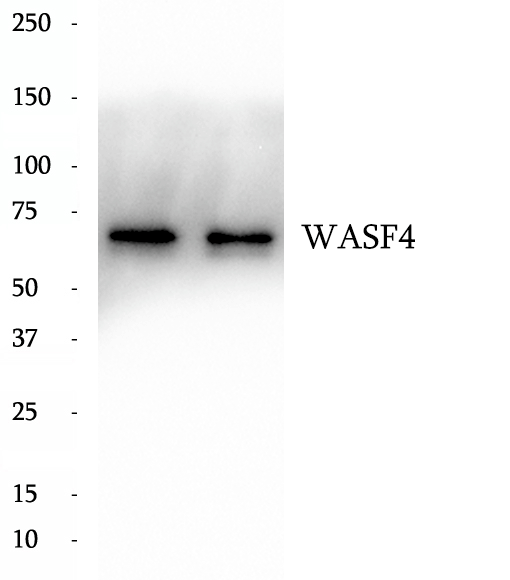
Anti-WASF4 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
WASF4, also named as SCAR2, belongs to the SCAR/WAVE family. WASF4 is a downstream effector molecule which involved in the transmission of signals from tyrosine kinase receptors and small GTPases to the actin cytoskeleton. The antibody is specific to WASF4.
|
|
BP60005
|
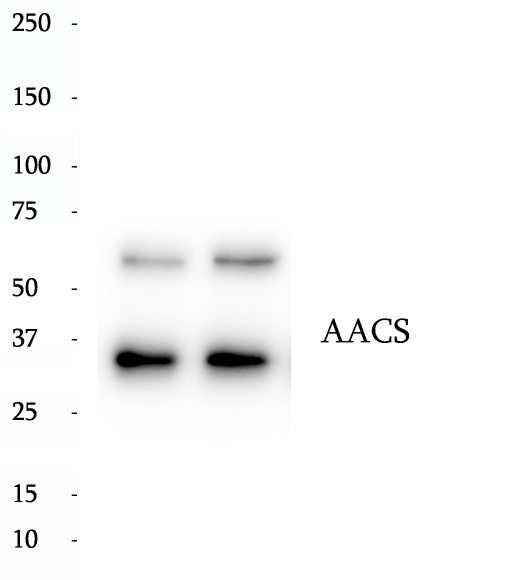
Anti-AACS antibody
|
|
|
|
|
AACS (acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase) is also named as ACSF1 and belonogs to the ATP-dependent AMP-binding enzyme family. In mammals, AACS is present in the cytosolic fractions of various tissues, especially lipogenic ones, and acetoacetate is known to be effectively incorporated into cholesterol and fatty acids. These results indicate that AACS may supply acetyl units to cytosolic compartment for cholesterol and/or fatty acid biosynthesis. It has 3 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP60669
|
Anti-Caspase 10 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Caspase-10 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CASP10 gene. This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein cleaves and activates caspases 3 and 7, and the protein itself is processed by caspase 8. Mutations in this gene are associated with apoptosis defects seen in type II autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.
|
|
BP60740
|
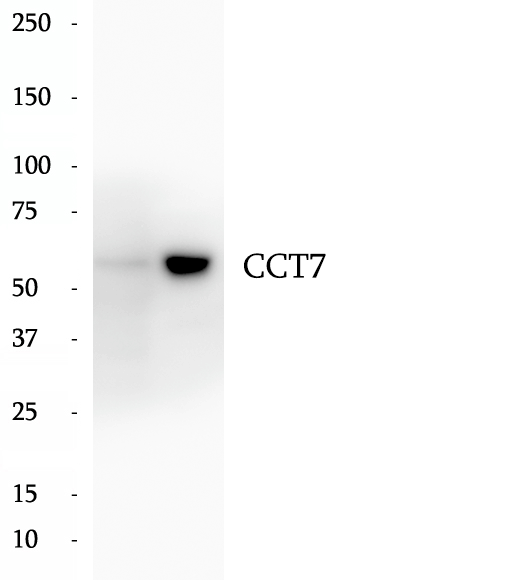
Anti-CCT7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
CCT7 is a subunit of CCT complex-a large cytosolic chaperonin complex composed of two hetero-oligomeric stacked rings able to interact with nascent polypeptides, which mediates protein folding in an ATP-dependent manner and prevents aggregation in eukaryotes. Each ring consists of eight different subunits (CCT1 to CCT8). CCT7 is involved in preventing aggregation of GPCRs and in regulating their expression, maturation, and transport to the cell surface.
|
|
BP61073
|
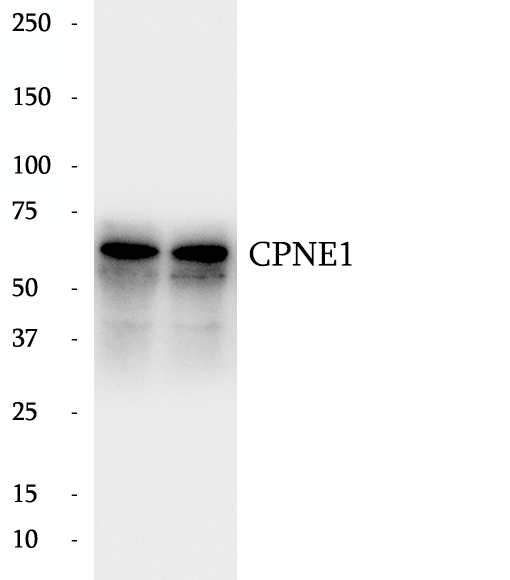
Anti-CPNE1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Copines are a family of evolutionarily conserved calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins. They contain two Ca (2+)- and phospholipid-binding domains known as C2 domains. Copines are potentially involved in regulating membrane trafficking and in protein-protein interactions.
|
|
BP64784
|
Anti-TBX4/5 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
T-box genes encode a family of transcription factors that have been identified in all metazoans and which play diverse roles during embryonic development. TBX5, a member of T-box family, has an essential role in the initiation of limb outgrowth and heart development. Genetic variation near TBX5 that associates with PR and/or QRS interval variation, which suggests that TBX5 plays a role in CCS function in the general population. Because 77 % amino acid sequence of TBX5 is identical to TBX4, this antibody recognizes both TBX4 and TBX5.
|
|
BP63619
|
Anti-Phospho-PTEN (Thr382/383) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
PTEN is one of the most critical tumor suppressors, which functions at different subcellular locations, including the plasma membrane and nucleus. The PTEN protein is located at different subcellular regions-PTEN at the plasma membrane suppresses PI3-kinase signaling in cell growth, whereas PTEN in the nucleus maintains genome integrity. At the plasma membrane, PTEN counteracts PI3 kinase signaling by dephosphorylating the potent second messenger PIP3 to PIP2. The loss of PTEN in cancer cells results in over-activation of AKT and mTOR signaling, leading to excessive stimulation of cell growth and inhibition of cell death. In the nucleus, PTEN functions in DNA repair, genome stability, and cell cycle control through associations with Rad51 and p53. PTEN stability is primarily regulated by phosphorylation of C-terminal tail domains (Thr366, Ser370, Ser380, Thr382, Thr383, and Ser385). The phosphorylation leads to a "closed" state of PTEN and maintains PTEN stability. Dephosphorylation of the C-terminal tail opens the PTEN phosphatase domain, thereby increasing PTEN activity. PTEN protein is of the apparent molecular mass expected for PTEN (55 kDa) and PTENα (70 kDa).
|
|
BP62105
|
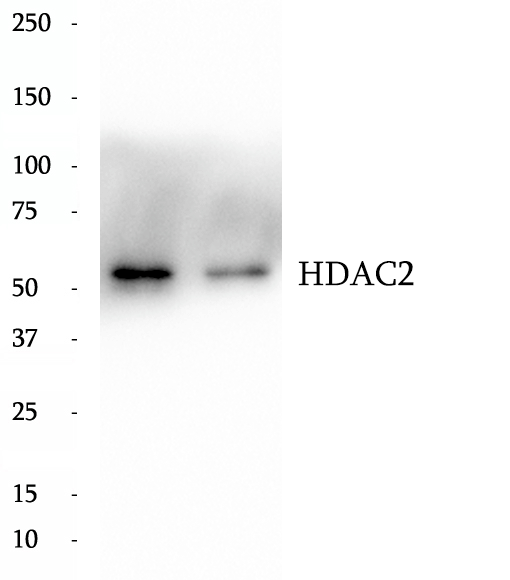
Anti-HDAC2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin.Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes, and are responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues at the N-terminal regions of core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). At least 4 classes of HDAC were identified. As a class I HDAC, HDAC2 was primarily found in the nucleus. HDAC2 forms transcriptional repressor complexes by associating with many different proteins, including YY1, a mammalian zinc-finger transcription factor. Thus, it plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against residues near the C terminus of human HDAC2.
|
|
BP64932
|
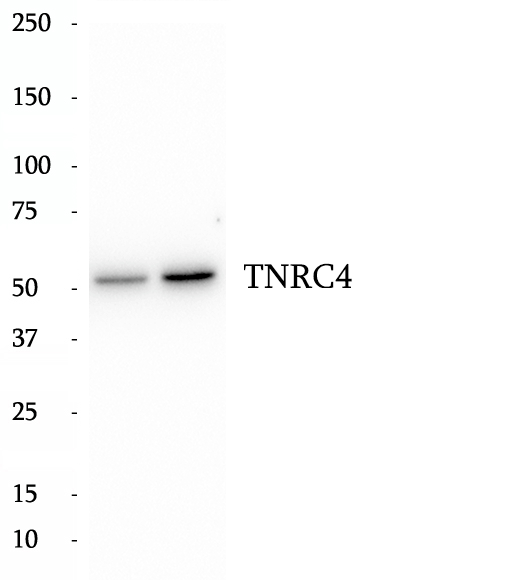
Anti-TNRC4 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
TNRC4, also named as BRUNOL1, CAGH4, ERDA4, or TNRC4, is a 465 amino acid protein, which contains three RRM (RNA recognition motif) domains and belongs to the CELF/BRUNOL family. TNRC4 localizes in the nucleus and is expressed in brain. TNRC4 as a RNA-binding protein is involved in the regulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing and mediates exon inclusion and/or exclusion in pre-mRNA that are subject to tissue-specific and developmentally regulated alternative splicing.
|
|
BP62687
|
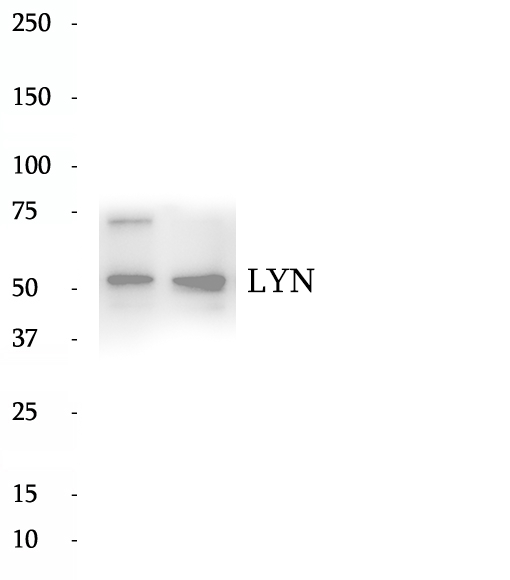
Anti-LYN antibody
|
|
|
|
|
LYN, also named as JTK8, p53Lyn and p56Lyn, belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family and SRC subfamily. It is a non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that transmits signals from cell surface receptors and plays an important role in the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses, hematopoiesis, responses to growth factors and cytokines, integrin signaling, but also responses to DNA damage and genotoxic agents. LYN is a component of the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) pathway.
|
|
BP63601
|
Anti-Phospho-P53 (Ser15) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The p53 tumor suppressor protein plays a major role in cellular response to DNA damage and other genomic aberrations. Activation of p53 can lead to either cell cycle arrest and DNA repair or apoptosis. DNA damage induces phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15 and Ser20 and leads to a reduced interaction between p53 and its negative regulator, the oncoprotein MDM2. p53 can be phosphorylated by ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK at Ser15 and Ser37. Phosphorylation impairs the ability of MDM2 to bind p53, promoting both the accumulation and activation of p53 in response to DNA damage.
|
|
BP63602
|
Anti-Phospho-P53 (Ser392) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
P53 is a 53 kDa protein that is activated in response to alteration of normal cell homeostasis, including DNA damage, nutrient starvation, heat shock, virus infection, pH change, hypoxia, and oncogene activation. P53 maintains genetic stability by regulating different processes, such as cell-cycle arrest, DNA synthesis and repair, programmed cell death, and energy metabolism. In non-stressed conditions these proteins bind p53, ubiquitylate it and target it for degradation by the proteasome. In stressed conditions the function of the MdM2-MdM4 complex is blocked by phosphorylation, protein-binding events and/or enhanced degradation. Phosphorylated at Ser-315 and Ser-392 by CDK2 in response to DNA-damage.
|
|
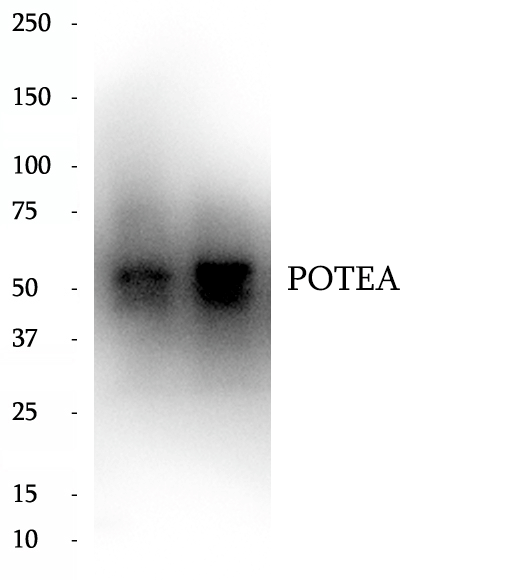
BP63765
|
Anti-POTEA antibody
|
|
|
|
|
POTEA also named as ANKRD26 like family A member 1 or POTE8 is a 498 amino acid protein, which contains five ANK repeats and belongs to the POTE family. POTEA has an important signaling function in the reproductive system.
|
|
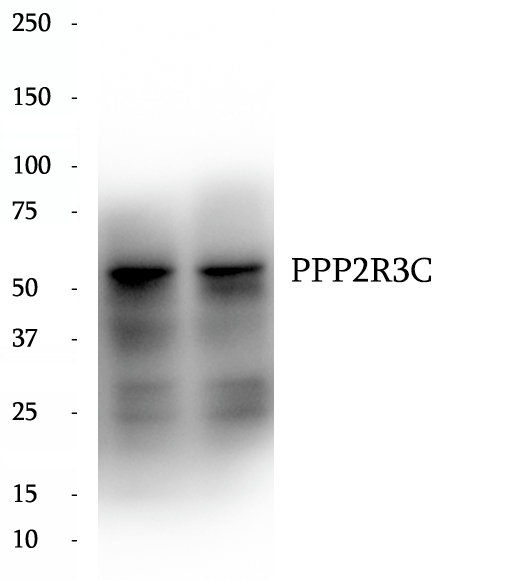
BP63798
|
Anti-PPP2R3C antibody
|
|
|
|
|
PPP2R3C (Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B'' subunit gamma) is also named as C14orf10, and G5PR. It may regulate MCM3AP phosphorylation through phosphatase recruitment and play a role in the activation-induced cell death of B-cells. It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 53 kDa and 40 kDa.
|
|
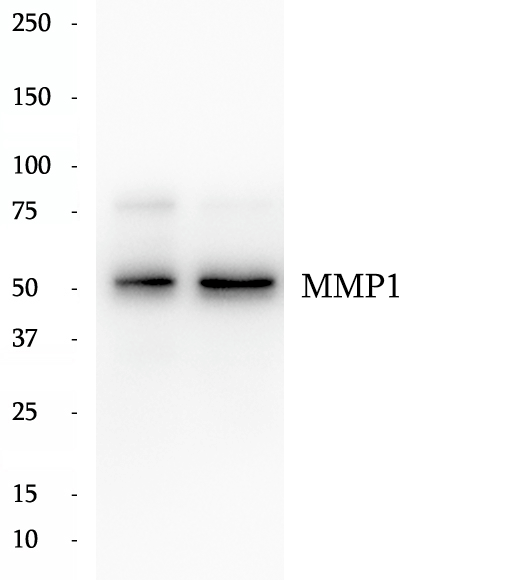
BP62874
|
Anti-MMP1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MMP1, also named as CLG, belongs to the peptidase M10A family. MMP is the main enzyme that cleaves fibrillar collagen, namely types I, II, III, VII, and X.It is involved in cell migration and invasion, and is frequently up-regulated in cancer cells. It can be cleavage to two major forms (22 kDa and 27 kDa) by undergoing autolytic,and the minor form (25 kDa) is the glycosylated form of the 22 kDa form. The 27 kDa form has no activity while the 22/25 kDa form can act as activator for collagenase.The sizes of pro-MMP-1 and active MMP-1 from human synovial fibroblasts have been reported as 52 to 56 kDa, depending on glycosylation, and 41 to 45 kDa, respectively.In addition,a band of 62-kDa observed in the current study is pro-MMp-1.
|


 antibody.gif)
 antibody.gif)
 antibody.gif)