|
BP61941
|
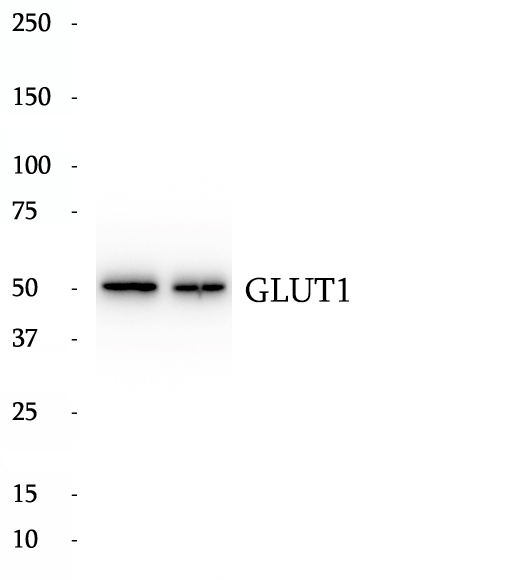
Anti-GLUT1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Glucose transporter 1 (or GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC2A1 gene. GLUT1 facilitates the transport of glucose across the plasma membranes of mammalian cells. This gene encodes a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. The encoded protein is found primarily in the cell membrane and on the cell surface, where it can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II. One good source of GLUT1 is erythrocyte membranes. GLUT1 accounts for 2 percent of the protein in the plasma membrane of erythrocytes. GLUT1, found in the plasma membrane of erythrocytes, is a classic example of a uniporter. After glucose is transported into the erythrocyte, it is rapidly phosphorylated, forming glucose-6-phosphate, which cannot leave the cell. Mutations in this gene can cause GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1, GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 2, idiopathic generalized epilepsy 12, dystonia 9, and stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis.
|
|
BP61841
|
Anti-GALK1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
GALK1, also named as GALK, belongs to the GHMP kinase family and GalK subfamily. GALK1, located on chromosome 17q24, encodes galactokinase and is involved in galactose metabolism. The molecular weight of GALK1 is 42 kDa.
|
|
BP62291
|
Anti-IDO1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
IDO1 is the target for therapy in a range of clinical settings, including cancer, chronic infections, autoimmune and allergic syndromes, and transplantation. Elevated IDO1 expression is a hallmark of major viral infections including HIV, HBV, HCV or influenza and also of major bacteria infections, such as Tb, CAP, listeriosis and sepsis. Pathogens are able to highjack the immunosuppressive effects of IDO1 and make use of them to facilitate their own life cycle. MW of IDO1 is 40-42kd.
|
|
BP63572
|
Anti-Phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade plays also a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. MEK1 and MEK2 activate p44 and p42 through phosphorylation of activation loop residues Thr202/Tyr204 and Thr185/Tyr187, respectively. Several downstream targets of p44/42 have been identified, including p90RSK and the transcription factor Elk-1. The antibody recognizes ERK2 phosphorylation sites Thr185 and Tyr187.
|
|
BP64599
|
Anti-SPON2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SPON2 (Spondin 2), also known as Mindin, is a member of the F-spondin family of secreted extracellular matrix proteins. This protein has been implicated in axon guidance, immune response and adhesion. SPON2 is essential in the initiation of the innate immune response and represents a unique pattern-recognition molecule in the ECM for microbial pathogens. It also functions as an integrin ligand for inflammatory cell recruitment and T-cell priming. Besides, SPON2 has been reported as a prognostic biomarker for ovarian and prostate cancer.
|
|
BP60674
|
Anti-Caspase 6 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Caspase-6 belongs to caspase family of cysteinyl-aspartate specific proteases.Precursor of CASP6 produces two subunits, large (18kDa) and small (16kDa) that dimerize. It cleaves poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, as well as lamins and is involved in the activation cascade of caspases responsible for apoptosis execution. Researches showed that CASP6 could be an early instigator of neuronal dysfunction and regulates B cell activation and differentiation into plasma cells by modifying cell cycle entry. IRAK3 is an important target for CASP6. It can reveal five bands of 28, 32, 36, 49, and 64 kDa in human neurons and fetal brain in western blot, the 32 and 28 kDa bands represent procaspase-6 and pro-arm caspase-6. Procaspase-6 is more abundant than pro-arm caspase-6 in adult tissue, whereas pro-arm caspase-6 is more abundant than pro-caspase-6 in fetal brain and cultured neurons. The higher molecular mass bands at 49 and 64 kDa likely represent dimers of p28 and p32.. In rat testis, it can be detected two bands of 34 kDa and 12 kDa or 14 kDa.
|
|
BP65079
|
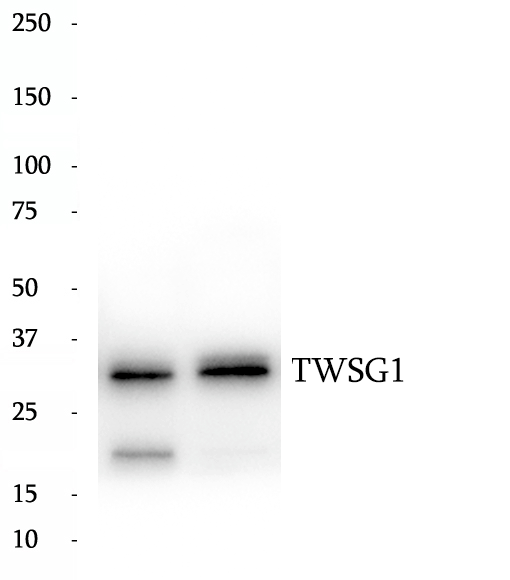
Anti-TWSG1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are potent morphogens that are involved in cell fate determination, proliferation, apoptosis and adult tissue homeostasis. Twisted gastrulation (TWSG1) is a secreted BMP binding protein that modulates BMP ligand availability in the extracellular space. Several in vitro studies point toward an important role of TWSG1 in the regulation of the immune system.
|
|
BP64516
|
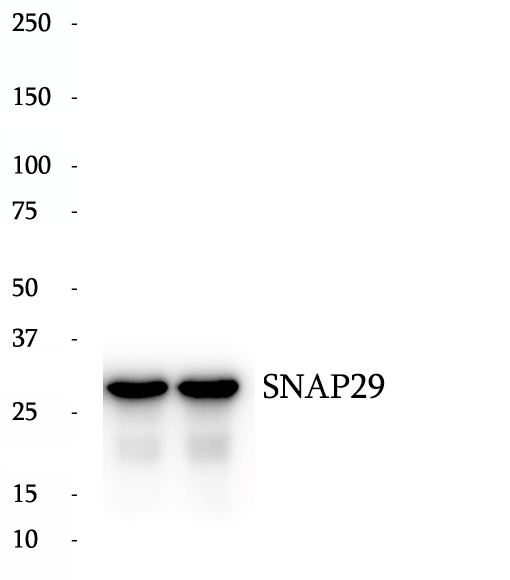
Anti-SNAP29 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SNAREs, soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor-attachment protein receptors, are essential proteins for fusion of cellular membranes. SNAREs localized on opposing membranes assemble to form a trans-SNARE complex, an extended, parallel four alpha-helical bundle that drives membrane fusion. SNAP29 is a SNARE involved in autophagy through the direct control of autophagosome membrane fusion with the lysososome membrane. SNAP29 plays also a role in ciliogenesis by regulating membrane fusions.
|
|
BP64933
|
Anti-TNS1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
TNS1, also named as TNS, may be involved in cell migration, cartilage development and in linking signal transduction pathways to the cytoskeleton. The antibody recognizes near the N-term of TNS1.
|
|
BP60170
|
Anti-Alpha-2-Macroglobulin antibody
|
|
|
|
|
alpha-2-macroglobulin, also known as α2-macroglobulin (α2M or A2M), is a protein abundant in the plasma of vertebrates and several invertebrates. A2M is an evolutionarily conserved arm of the innate immune system. It also mediates the proliferation of T cells and macrophages. A2M acts as a nonspecific protease inhibitor involved in the host defense mechanism that inactivates both endogenous and exogenous proteases, including trypsin, thrombin and collagenase. Even though A2M is produced predominantly by the liver, it may also be expressed in the reproductive tract, heart, and brain, and may have important roles in many physiological processes and medical illnesses including Alzheimer's disease.
|
|
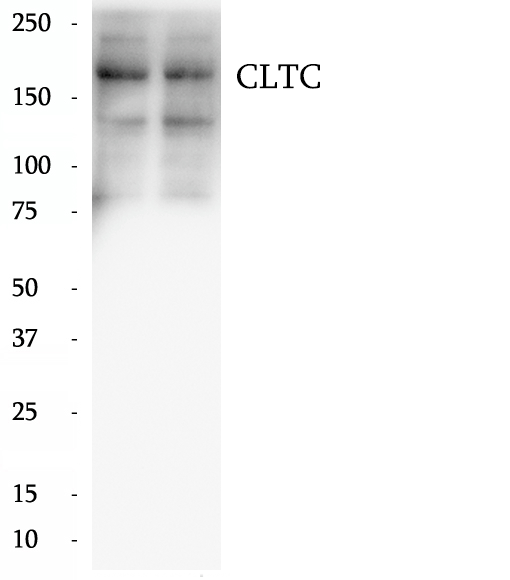
BP60988
|
Anti-CLTC antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Clathrin is the major protein of the polyhedral coat of coated pits and vesicles which entrap specific macromolecules during receptor-mediated endocytosis. The clathrin molecule has a triskelion shape. Each clathrin triskelion is composed of three identical heavy chains (CLTC) (160-190 kDa) and three light chains of two types, LCA (CLTA) and LCB (CLTB) (30-40 kDa). The heavy chain provides the structural backbone of the clathrin lattice.
|
|
BP62441
|
Anti-JMJD3 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
JMJD3, also known as KDM6B, is a 1643 amino acid protein, which belongs to the UTX family. JMJD3 is a Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code are transcription activators, being specific H3K27me3 demethylases. JMJD3 is involved in many cellular process such as development, differentiation, senescence and aging by p16, p53 and RB pathways and finally inflammation. Depending on cancer type, JMJD3 expression is increased (prostate and breast cancers, melanoma, gliomas, renal cell carcinomaor decreased (lung, liver, pancreatic, colon and colorectal cancers. This role in carcinogenesis has allowed the development of "epidrugs" to modulate JMJD3 expression.
|
|
BP61514
|
Anti-EIF5B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Translation initiation requires the delivery of the initiator methionine tRNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit. The initiator methionine tRNA is delivered by the heterotrimeric complex EIF2 in a ternary complex with GTP that interacts with the 40S subunit. The resulting complex then binds to an mRNA and scans for the AUG start codon. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (EIF5B) plays a role in recognition of the AUG codon in conjunction with translation factor eIF2, which functions to general translation initiation by promoting the binding of the formylmethionine-tRNA to ribosomes, and promotes joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit. A single crossreactive polypeptide of 175 kDa was detected, whereas the predicted size of the protein was 139 kDa. This size discrepancy may be the result of posttranslational modifications of EIF5B or, perhaps more likely, of unusual behavior in SDS-PAGE caused by the highly charged N-terminal region of EIF5B.
|
|
BP62111
|
Anti-HDAC6 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin. At least 4 classes of HDAC were identified. HDAC6 is a member of the class II mammalian histone deacetylases. It possesses two separate putative catalytic domains. Both catalytic domains are fully functional HDACs and contribute independently to the overall activity of HDAC6 protein. A very potent NES is present at the amino-terminus of HDAC6, which was found to play an important role in regulating the shuttling of HDAC6 protein between cytoplasm and nucleus. The shuttling process may be a critical regulatory mechanism of HDAC6 function. The expression of HDAC6 is tightly linked to the state of cell differentiation. HDAC6 may participate in coordinating expression of a group of genes involved in the remodelling of chromatin during cell differentiation. HDAC6 has some splicing variants such as P114 (~130kd), P131 (~160kd).This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against residues near the C terminal of human HDAC6. The calculated molecular weight of HDAC6 is 130 kDa, but the modified the HDAC6 is about 150-160 kDa.
|
|
BP63582
|
Anti-Phospho-JAK3 (Tyr980/981) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
JAK3 belongs to the Janus kinase family of receptor-associated tyrosine kinases located in cytoplasm adjacent to the plasma membrane. Janus kinase family comprise four tyrosine (Tyr) kinases (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and Tyk2). In the cytoplasm, JAKs play a pivotal role in signal transduction via its association with type I and type II cytokine receptors, which include receptors for interleukins (ILs), interferons (IFNs), and hormones such as leptin. Interaction of a cytokine with its membrane-bound receptor complex triggers activation of receptor-bound JAKs, which phosphorylate the receptor on key cytoplasmic Tyr residues. These act as docking sites for SH2 domain-mediated interactions with STAT proteins. Receptor-bound STATs are then phosphorylated on conserved Tyr residues within their C terminal domains prior to dissociation from the receptor and formation of homo- or heterodimers. These translocate to the nucleus, bind target gene promoters, and stimulate target gene transcription.
|
|
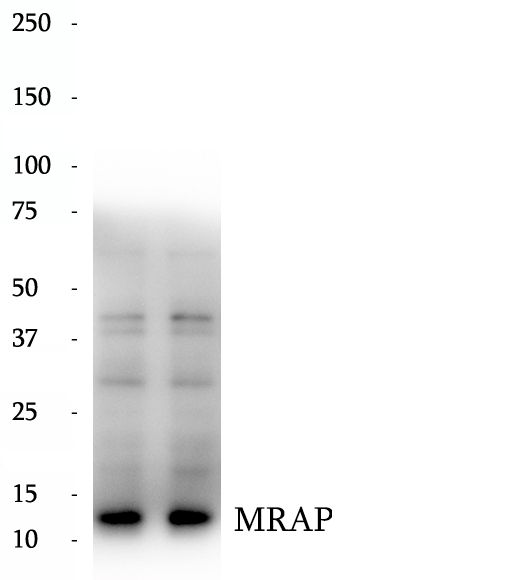
BP62914
|
Anti-MRAP antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MRAP, also named as C21orf61, FALP and B27, is required for MC2R expression in certain cell types. MRAP is involved in the processing, trafficking or function of MC2R. MRAP may be involved in the intracellular trafficking pathways in adipocyte cells. Mutation of MRAP will cause glucocorticoid deficiency type 2 (GCCD2) which known as familial glucocorticoid deficiency type 2 (FGD2). The antibody can recognize the isoform1,isoform2 and isoform4.
|
|
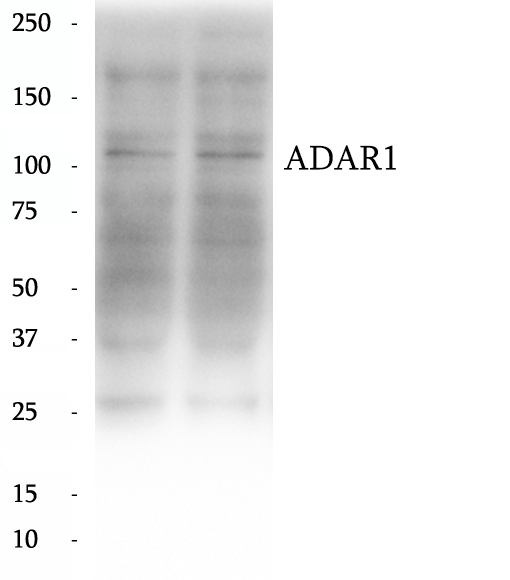
BP60064
|
Anti-ADAR1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ADAR1 is also named as ADAR1, DSRAD, G1P1, IFI4. It convert selected adenosine residues into inosine in substrate RNAs containing a relatively short dsRNA region. The human ADAR1 gene specifies two size forms of RNA-specific adenosine deaminase, an IFN inducible ∼150 kDa protein and a constitutively expressed N-terminally truncated ∼110 kDa protein, encoded by transcripts with alternative exon 1 structures that initiate from different promoters. It has 5 isoforms produced by alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing. Defects in ADAR are a cause of dyschromatosis symmetrical hereditaria (DSH).ADAR1 can form respective homodimers, and this association is essential for its enzymatic activities.
|
|
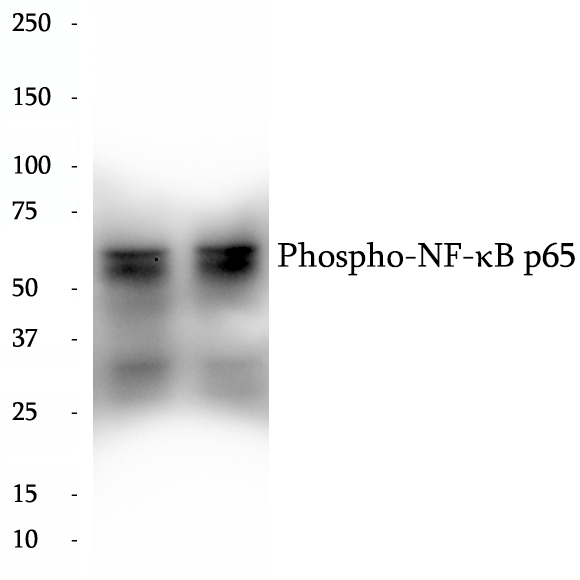
BP65429
|
Anti-Phospho-NF-κB p65 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Nuclear factor k B (NF-kB) is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein complex which regulates the expression of viral genomes, including the human immunodeficiency virus, and a variety of cellular genes, particularly those involved in immune and inflammatory responses. The members of the NF-kB family in mammalian cells include the proto-oncogene c-Rel,p50/p105 (NFkB1), p65 (RelA), p52/p100 (NFkB2), and RelB. All of these proteins share a conserved 300-amino acid region known as the Rel homology domain which is responsible for DNA binding, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of NF-kB. The p65 subunit is a major component of NF-kB complexes and is responsible for trans-activation. NF-kB heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kB p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. The inhibitory effect of IkB upon NF-kB the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kB complex. It associates with chromatin at the NF-kB promoter region via association with DDX1.
|
|
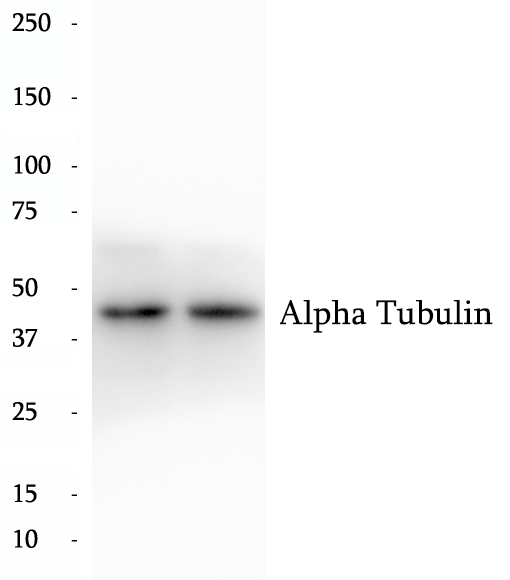
BP60168
|
Anti-Alpha Tubulin antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.
|
|
BP63610
|
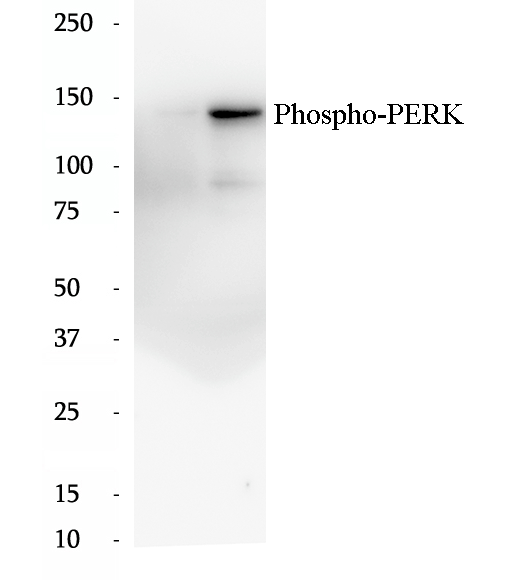
Anti-Phospho-PERK/EIF2AK3 (Ser719) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
EIF2AK3 encodes the protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK), a key regulator of the unfolded protein response (UPR) in response to ER stress. Under ER stress conditions, activation of PERK is triggered by the dissociation of glucose-regulated protein (GRP) 78 (also known as BiP) from its luminal domain, followed by oligomerization and autophosphorylation. Phosphorylated PERK subsequently phosphorylates eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eif2α), to attenuate global protein translation and reduce incoming ER protein load via upregulated ER chaperone expression.
|


 antibody.gif)







 antibody.gif)