|
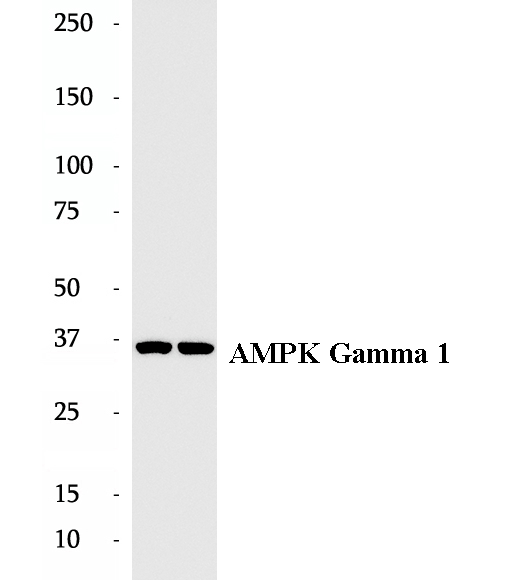
BP60187
|
Anti-AMPK Gamma 1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 1 non-catalytic subunit (PRKAG1, synonyms: AMPKG, MGC8666) is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic and subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and iAMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a highly conserved heterotrimeric serine/threonine kinase widely characterised as a sensor of cellular energetic stress. AMPK is a heterotrimeric complex consisting of a catalytic α-subunit and two regulatory subunits (β and γ). AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. AMPK gamma 1 is one of the gamma regulatory subunits of AMPK.
|
|
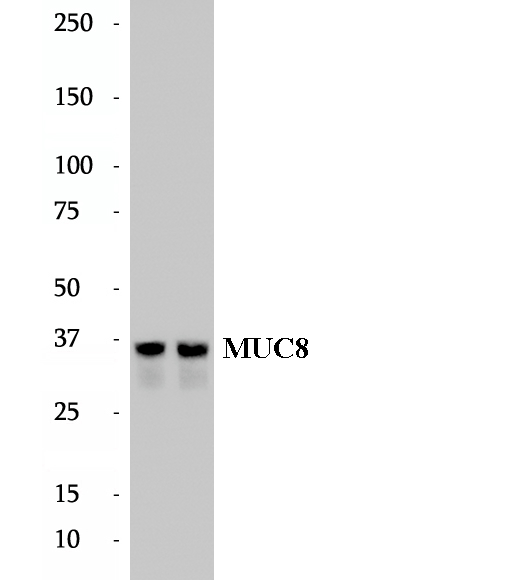
BP62970
|
Anti-MUC8 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Mucin glycoproteins (Mucins) are major constituents of the glycocalyx that covers mucosal epithelium. MUC8 is one of the major mucins in the ethmoid mucosa and is upregulated by chronic inflammation. TNFa, IL-1b and a combination of both can significantly increase Mucin 8 mRNA levels, suggesting that a mixture of inflammatory mediators can synergistically increase secretion of mucin in human nasal epithelium. This antibody is specific to MUC8.
|
|
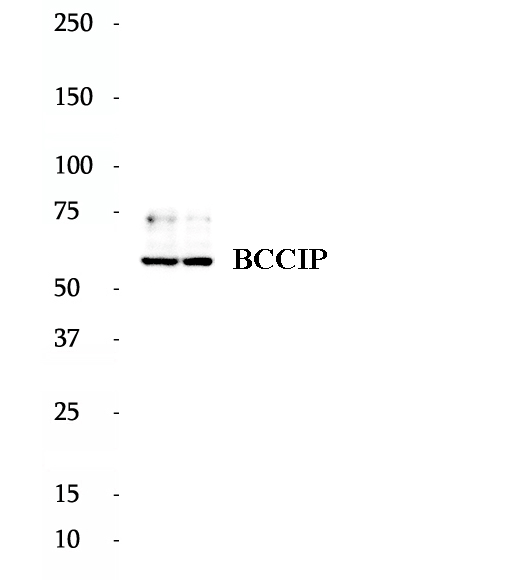
BP60447
|
Anti-BCCIP antibody
|
|
|
|
|
BCCIP (or TOK1) is isolated as a BRCA2- and CDKN1A (p21)-interacting protein and is implicated in homologous recombination (HR) pathway and inhibition of DNA replication stress. BCCIP is an evolutionarily conserved nuclear protein with multiple interacting domains. BCCIP deficiency in mice impaired embryonic and postnatal neural development, causing severe ataxia, cerebral and cerebellar defects, and microcephaly, which are associated with spontaneous DNA damage and subsequent cell death in the proliferative cell populations of the neural system during embryogenesis. BCCIP is essential for maintaining the transactivation activity of wild type p53 suggesting a potential role of BCCIP in cancer etiology.
|
|
BP60586
|
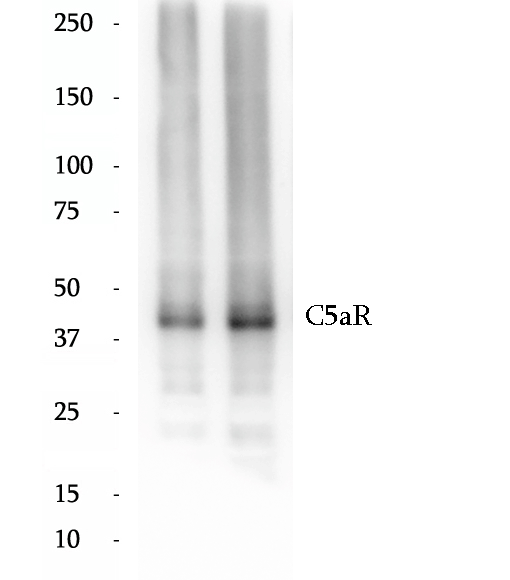
Anti-C5aR antibody
|
|
|
|
|
C5aR, also named as CD88, is a G protein-coupled receptor for the anaphylatoxin C5a, a cleavage product of the complement cascade. The C5a ligand is a proinflammatory component of host defense. C5aR is activated upon binding of the C5a molecule. Receptor activation stimulates chemotaxis, granule enzyme release, intracellular calcium release and superoxide anion production. The deduced sequence of C5aR contains 350 amino acids, giving a calculated molecular weight of 39 kDa. C5aR has an N-linked glycosylation site in the N-terminal extracellular domain. The apparent molecular weight of C5aR is about 40-52 kDa.
|
|
BP62558
|
Anti-L2HGDH antibody
|
|
|
|
|
L2HGDH (L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial) is also named as duranin, C14orf160 and belongs to the L2HGDH family. The putative L2HGDH is predicted to be targeted to the mitochondria where its mitochondrial targeting sequence is presumably removed. Defects in L2HGDH are the cause of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (L2HGA). It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 50 kDa and 48 kDa. L2HGDH also can be detected as ~45kD due to the 51aa transit peptide cleaved.
|
|
BP60021
|
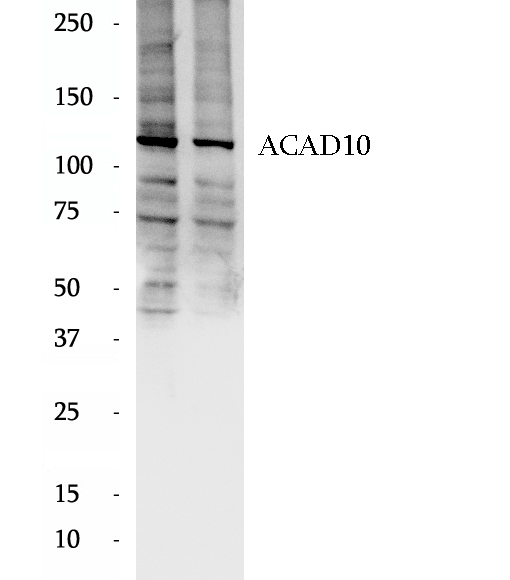
Anti-ACAD10 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ACAD10 (Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 10) belongs to the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family. ACAD10 has significant activity towards the branched-chain substrates R and S, 2 methyl-C15-CoA and is highly expressed in fetal but not adult brain. This pattern of expression is similar to that of LCAD, another ACAD previously shown to be involved in long branched chain fatty acid metabolism. It has 4 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP62113
|
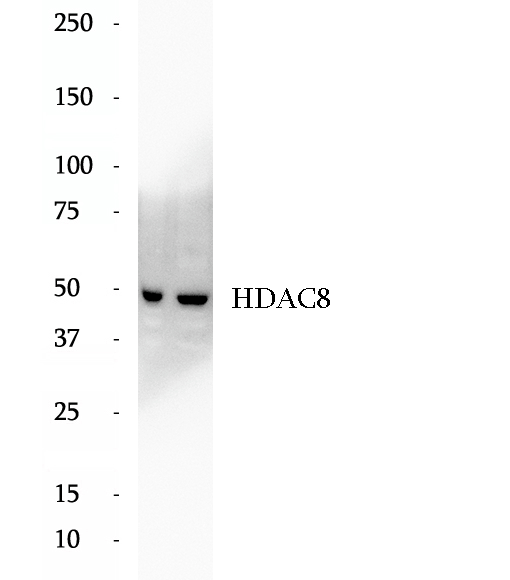
Anti-HDAC8 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin. At least 4 classes of HDAC were identified. As a class I HDAC, HDAC 8 was primarily found in the nucleus. It catalyzes the deacetylation of lysine residues in the histone N-terminal tails and represses transcription in large multiprotein complexes with transcriptional co-repressors. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against full length HDAC8 of human origin.
|
|
BP62668
|
Anti-LRWD1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
LRWD1 contains 3 LRR (leucine-rich) repeats and 5 WD repeats. LRWD1 is phosphorylated upon DNA damage by ATM or ATR. The antibody recognize the N-term of LRWD1.
|
|
BP61159
|
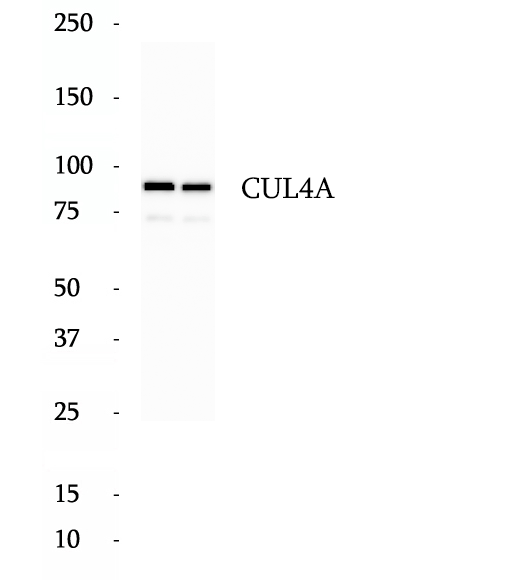
Anti-CUL4A antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Cullin proteins assemble a large number of RING E3 ubiquitin ligases, participating in the proteolysis through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Two cullin 4 (CUL4) proteins, CUL4A (87 kDa) and CUL4B (104 kDa), have been identified. The two CUL4 sequences are 83% identical. They target certain proteins for degradation by binding protein DDB1 to form a CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase complex with DDB. They form two individual E3 ligases, DDB1-CUL4ADDB2 and DDB1-CUL4BDDB2 in this process. CUL4A appeared in both the nucleus and the cytosol, suggesting a more complex mechanism for entering the nucleus. CUL4B is localized in the nucleus and facilitates the transfer of DDB1 into the nucleus independently of DDB2.
|
|
BP62745
|
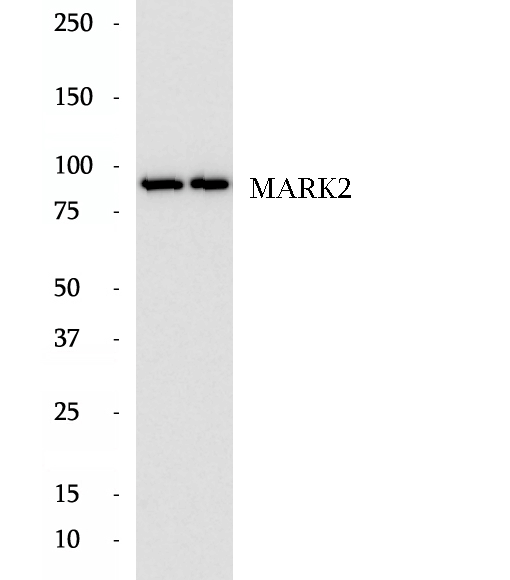
Anti-MARK2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MARK2 is also named as EMK1 (ELKL motif kinase 1), Par1b and belongs to the CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. Par1b/MARK2 plays a critical role in neuronal polarity in the process of axon specification from multiple candidate neurites using primary cultures of mammalian hippocampal neurons. It has 16 isoforms produced by alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing with the molecular mass of 77-90kDa and can exsit as a dimer.
|
|
BP64333
|
Anti-SEC6 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Exoc3 (Sec6) is a component of the exocyst (Sec6/8) complex involved in vesicle trafficking at neural synapses and vesicle targeting in polarized epithelial cells. Though best characterized in yeast, the component proteins and functions of exocyst complex have been demonstrated to be highly conserved in higher eukaryotes. This complex is composed of eight proteins (Sec3, Sec5, Sec6, Sec8, Sec10, and Sec15, Exo70 and Exo84), with molecular weights ranging from 70 to 144 kDa.
|
|
BP61235
|
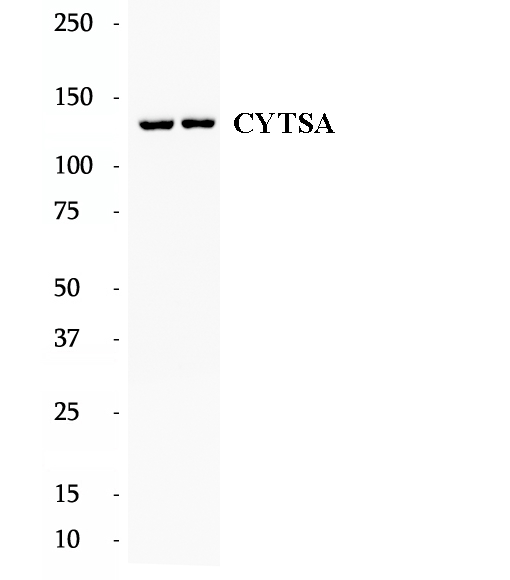
Anti-CYTSA antibody
|
|
|
|
|
CYTSA, also named as SPECC1L or KIAA0376, is a 1117 amino acid protein, which contains one CH domain and belongs to the cytospin-A family. CYTSA localizes in the cytoplasm and is involved in cytokinesis and spindle organization. CYTSA may play a role in actin cytoskeleton organization and microtubule stabilization, hence it is required for proper cell adhesion and migration.
|
|
BP65369
|
Anti-ZCCHC6 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ZCCHC6 also named as KIAA1711 ,HS2 or TUT7 is a 1495 amino acid protein, which contains threes CCHC-type zinc fingers and two PAP-associated domains. A member of the DNA polymerase type-B-like family, ZCCHC6 as a uridylyltransferase that mediates RNA uridylation.
|
|
BP64774
|
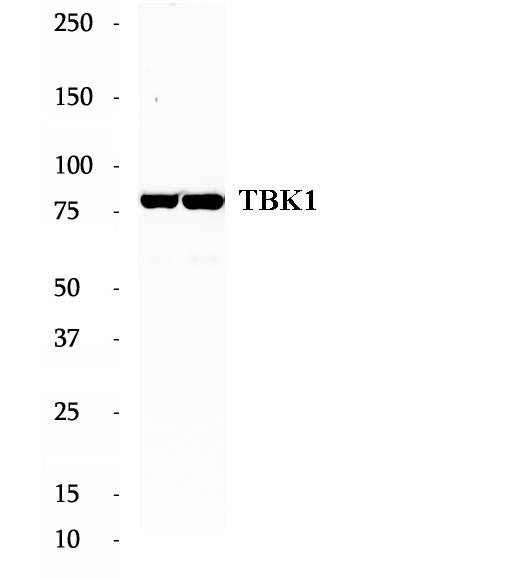
Anti-TBK1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
TBK1, also named as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor NF-kB activator (TANK)-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), NF-kB-activating kinase (NAK), T2K, is a multimeric kinase that modulates inflammation and autophagy. It is a ubiquitously expressed serine-threonine kinase belonging to the 'noncanonical IkB kinases' (IKKs) recognized for its critical role in regulating type I IFN production. And TBK1 is an important player in yet another critical cellular function, autophagy. This antibody is specific for TBK1.
|
|
BP62618
|
Anti-LILRB1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LILRB1 gene.
|
|
BP64475
|
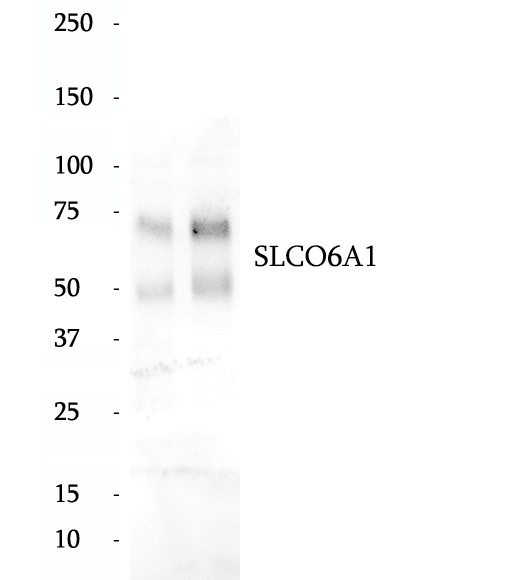
Anti-SLCO6A1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SLC6A1 epileptic encephalopathy is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by the loss-of-function of one copy of the human SLC6A1 gene.
|
|
BP61737
|
Anti-FIS1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Mitochondrial fission 1 protein (FIS1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FIS1 gene on chromosome 7. This protein is a component of a mitochondrial complex, the ARCosome, that promotes mitochondrial fission. Its role in mitochondrial fission thus implicates it in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology, the cell cycle, and apoptosis. By extension, the protein is involved in associated diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and cancers.
|
|
BP62292
|
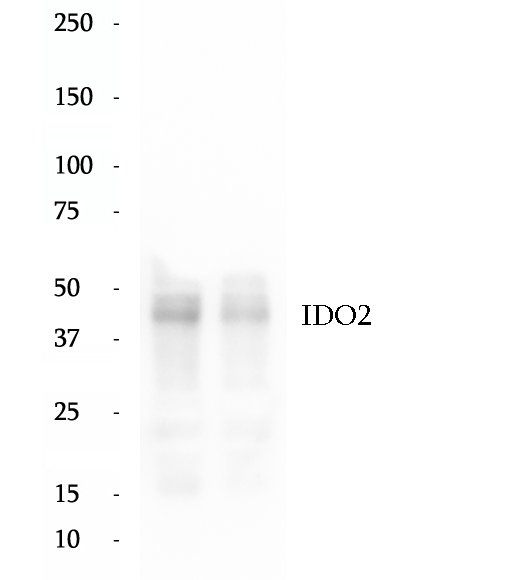
Anti-IDO2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
IDO2, also named as INDOL1, catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan catabolism. IDO2 gene has two isoforms with MW 45 kDa and 20 kDa.
|
|
BP65428
|
Anti-Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MTOR, also named as FRAP1, FRAP, FRAP2 and RAPT1, belongs to the PI3/PI4-kinase family.MTOR is a Ser/Thr protein kinase that functions as an ATP and amino acid sensor to balance nutrient availability and cell growth. MTOR is kinase subunit of both mTORC1 and mTORC2, which regulate cell growth and survival in response to nutrient and hormonal signals. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino-acids. mTORC2 is also activated by growth factors, but seems to be nutrient-insensitive. mTORC2 seems to function upstream of Rho GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton, probably by activating one or more Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors. mTORC2 promotes the serum-induced formation of stress-fibers or F-actin. mTOR is phosphorylated at Ser2448 via the PI3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway and autophosphorylated at Ser2481. mTOR plays a key role in cell growth and homeostasis and may be abnormally regulated in tumors.
|
|
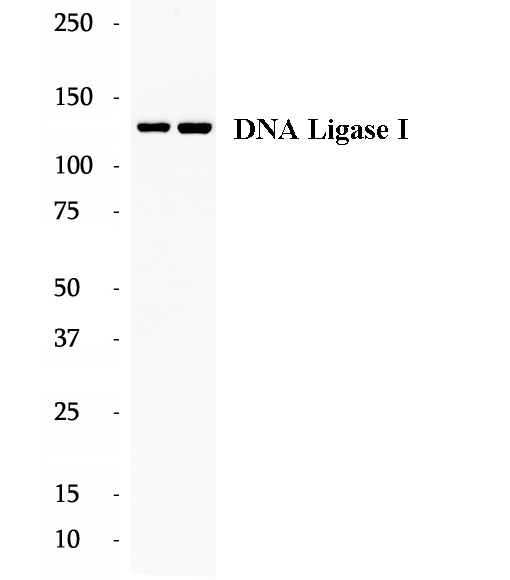
BP61363
|
Anti-DNA Ligase I antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DNA ligase I (LIG1) joins DNA strand breaks during DNA replication and repair transactions and contributes to genome integrity. 18051-1-AP is raised agains the C-terminal 670-919 aa residues of thehuman DNA ligase 1.
|






 antibody.gif)