|
BP69326
|
HRP Anti-Beta Tubulin antibody
|
|
|
|
|
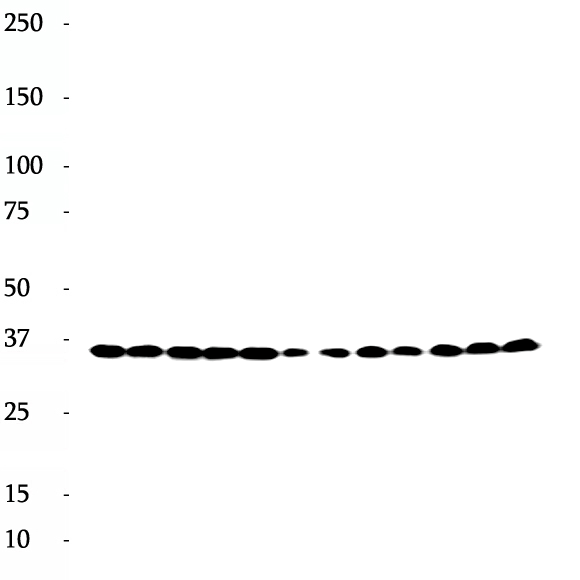
There are five tubulins in human cells: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon. Tubulins are conserved across species. They form heterodimers, which multimerize to form a microtubule filament. An alpha and beta tubulin heterodimer is the basic structural unit of microtubules. The heterodimer does not come apart, once formed. The alpha and beta tubulins, which are each about 55 kDa MW, are homologous but not identical. Alpha, beta, and gamma tubulins have all been used as loading controls. Tubulin expression may vary according to resistance to antimicrobial and antimitotic drugs.
|
|
BP69330
|
HRP Anti-GAPDH antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) catalyzes the phosphorylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate during glycolysis. GAPDH participates in nuclear events including transcription, binding RNA, RNA transportation, DNA replication, DNA repair and apoptosis. Being stably and constitutively expressed at high levels in most tissues and cells, GAPDH is considered a housekeeping protein. It is widely used as a control for RT-PCR and also loading control in electrophoresis and Western blotting. GAPDH is normally expressed in cellular cytoplasm or membrane, but can occasionally translocate to the nucleus after the addition of post-translational modifications such as S-nitrosylation. This antibody is raised against full length GAPDH of human origin. It can recognize the 36 kDa GAPDH protein in most cells/tissues. In addition, a band below 36 kDa can always be detected as the isoform or spliced product of GAPDH . Please note that some physiological factors, such as hypoxia and diabetes, increase GAPDH expression in certain cell types.
|
|
BP63149
|
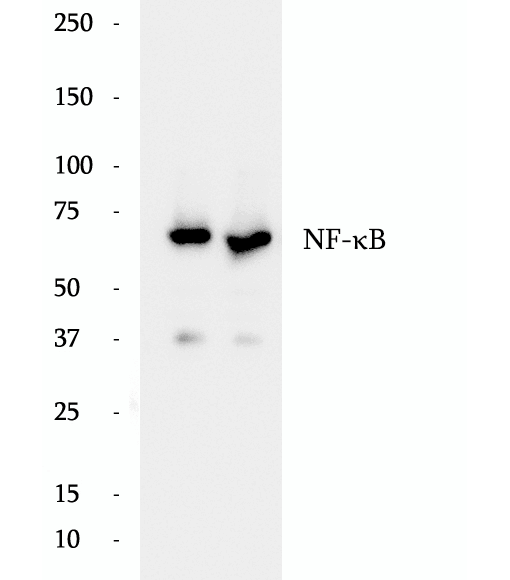
Anti-NF-κB p65 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Nuclear factor k B (NF-kB) is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein complex which regulates the expression of viral genomes, including the human immunodeficiency virus, and a variety of cellular genes, particularly those involved in immune and inflammatory responses. The members of the NF-kB family in mammalian cells include the proto-oncogene c-Rel,p50/p105 (NFkB1), p65 (RelA), p52/p100 (NFkB2), and RelB. All of these proteins share a conserved 300-amino acid region known as the Rel homology domain which is responsible for DNA binding, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of NF-kB. The p65 subunit is a major component of NF-kB complexes and is responsible for trans-activation. NF-kB heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kB p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. The inhibitory effect of IkB upon NF-kB the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kB complex. It associates with chromatin at the NF-kB promoter region via association with DDX1. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against residues near the N terminus of human RELA.
|
|
BP62413
|
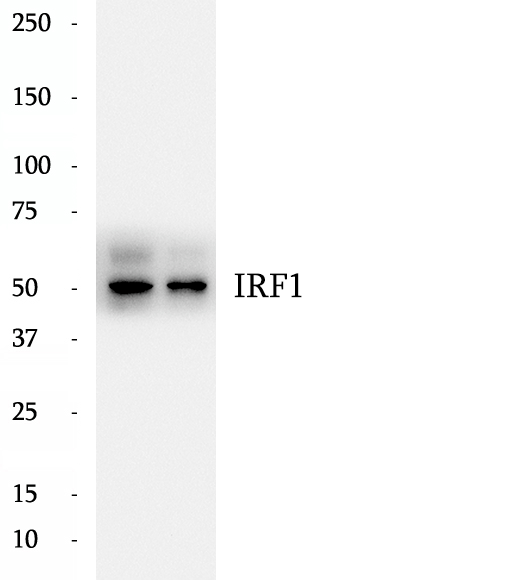
Anti-IRF1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
IRF1, also named as IFN regulatory factor 1, is a 325 amino acid protein, which belongs to the IRF family. IRF1 as a transcriptional regulator which displays a remarkable functional diversity in the regulation of cellular responses. The calculated molecular weight of IRF1 is 37 kDa, but the modified IRF1 protein is about 45-50 kDa.
|
|
BP64255
|
Anti-S100P antibody
|
|
|
|
|
S100P protein is a relatively small (95 amino acid) isoform of the S100 protein family that was first isolated from human placenta. Overexpression of S100P has been detected in several cancers such as breast, colon, prostate, pancreatic and lung carcinomas, and the protein has been functionally implicated in carcinogenic processes. S100P protein is widely expressed in both normal and neoplastic tissues. It clearly shows ectopic expression in some cancers. Based on the high expression in certain tumors, S100P could represent a potential target for novel diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
|
|
BP63366
|
Anti-P5CS antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS), also named as GSAS, P5CS, PYCS, catalyzes the ATP and the NAD (P)H-dependent conversion of L-glutamate to glutamic gamma-semialdehyde (GSA) which is the metabolic precursor for proline biosynthesis. It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP64872
|
Anti-TJAP1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
TJAP1, also named as PILT and TJP4, is colocalized at the tight junctions. TJAP1 has some forms with MW 60 kDa (native) and 86-90 kDa (modified).
|
|
BP63853
|
Anti-PROX1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Prospero homeobox protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PROX1 gene. The Prox1 gene is critical for the development of multiple tissues. Prox1 activity is necessary and sufficient to specify a lymphatic endothelial cell fate in endothelial progenitors located in the embryonic veins.
|
|
BP64136
|
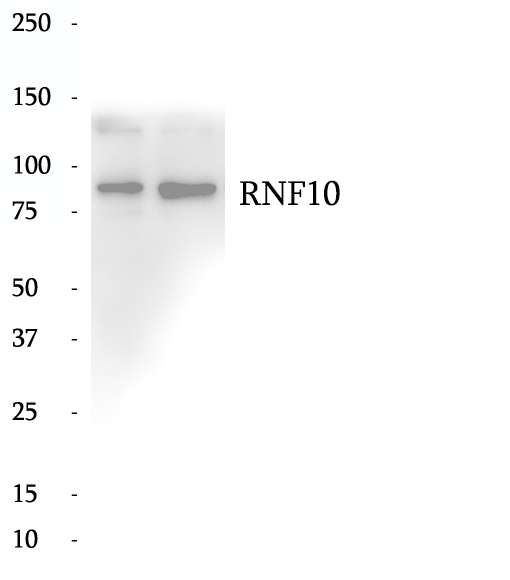
Anti-RNF10 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
RING finger (C3HC4-type zinc finger) is a variant zinc finger motif present in a new family of proteins including transcription regulators. RNF10 (RING finger protein 10), a 90-kDa protein, contains a ring finger motif which is known to be involved in protein-protein interactions. RNF10 regulates myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) expression and is required for myelin formation, therefore, participates in the peripheral nerve development and Schawnn cell differentiation. RNF10 is also involved in activation of p21WAF1 promoter via its activity as transcriptional factor.
|
|
BP60981
|
Anti-CLOCK antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Circadian locomoter output cycles protein kaput (CLOCK), also named as BHLHE8 or KIAA0334, is a 846 amino acid protein, which contains one bHLH domain, one PAC domain, and two PAS domains. CLOCK localizes in the nucleus and cytoplasm. CLOCK) is expressed in all tissues examined including spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, ovary, small intestine, colon, leukocytes, heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas. ARNTL/2-CLOCK heterodimers activate E-box element (5'-CACGTG-3') transcription of a number of proteins of the circadian clock, such as PER1 and PER2. The calculated molecular weight of CLOCK is 95kDa, we detected a 95-110 kDa protein by western blot. Our result is similar to the result of reseach paper.
|
|
BP61493
|
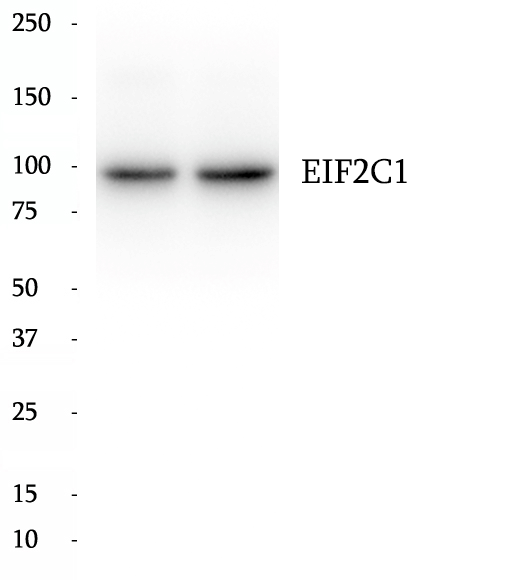
Anti-EIF2C1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
EIF2C1, also named as AGO1, belongs to the argonaute family and Ago subfamily. EIF2C1 is required for RNA-mediated gene silencing (RNAi). It binds to short RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) or short interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and represses the translation of mRNAs which are complementary to them. Lacks endonuclease activity and does not appear to cleave target mRNAs. EIF2C1 may also be required for transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) of promoter regions which are complementary to bound short antigene RNAs (agRNAs). The antibody is specific to EIF2C1.
|
|
BP62122
|
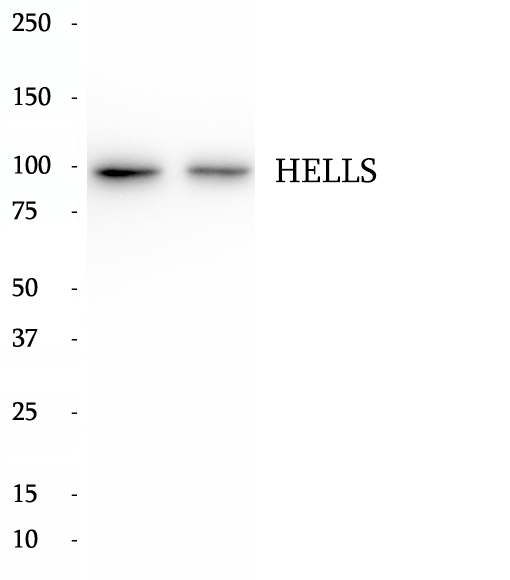
Anti-HELLS antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Lymphoid-specific helicase (HELLS) is a member of the SNF2 family of chromatin remodeling proteins that is required for development and survival. It's required for de novo or maintenance DNA methylation, which mediated the silencing of the imprinted CDKN1C gene. Also it involved in formation and organization of heterochromatin that regulate transcription and mitosis.
|
|
BP63466
|
Anti-PDE6B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
PDE6 is a cGMP-specific PDE family and presents multicomponent enzyme complexes. The rod PDE6 enzyme is comprised of two catalytic subunits (PDE6A and PDE6B) and it is expressed in human lungs is also named as PDEB and belongs to the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family. PDE6B also has a C-terminal CAAX motif for posttranslational processing involving lipidation, proteolysis, and carboxymethylation and congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant type 2 (CSNBAD2).
|
|
BP63692
|
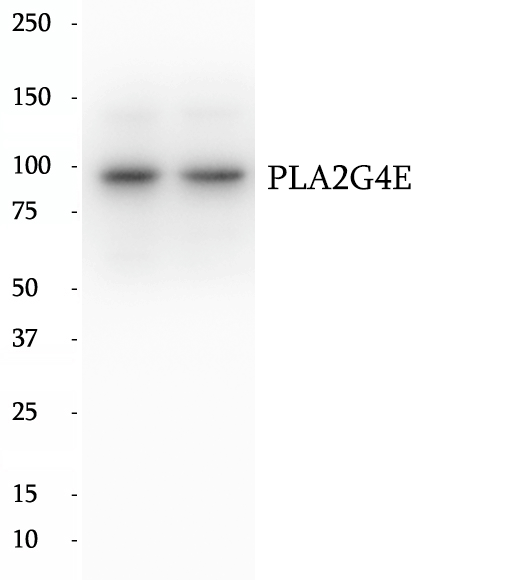
Anti-PLA2G4E antibody
|
|
|
|
|
PLA2G4E (Phospholipase A2 group IVE), also known as cPLA2-epsilon. Calcium-dependent N-acyltransferase is involved in the biosynthesis of N-acyl ethanolamines (NAEs) in the brain to the amine group of phosphatidylethanolamine (fatty acyl acceptor) to generate N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE). Similarly can use plasmenylethanolamine as a fatty acyl acceptor to form N-acyl plasmenylethanolamine (N-Acyl-PlsEt). Both NAPE and N-Acyl-PlsEt can serve as precursors of bioactive NAEs like N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine also called anandamide.
|
|
BP62731
|
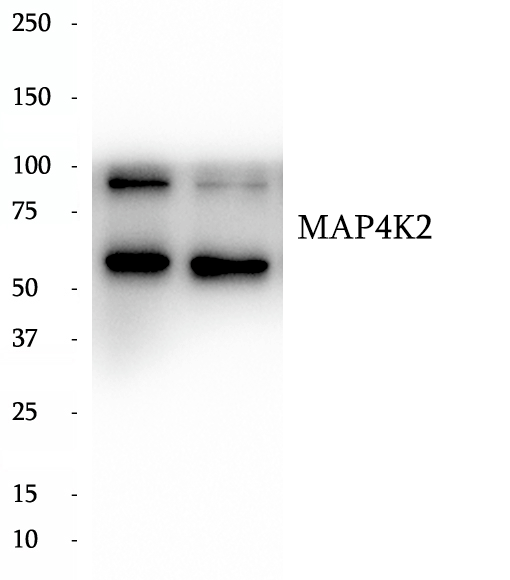
Anti-MAP4K2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MAP4K2,also named as GCK and RAB8IP, belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family and STE20 subfamily. It enhances MAP3K1 oligomerization, which may relieve amino-terminal mediated MAP3K1 autoinhibition and lead to activation following autophosphorylation. MAP4K2 may play a role in the regulation of vesicle targeting or fusion. This antibody is specific to MAP4K2.
|
|
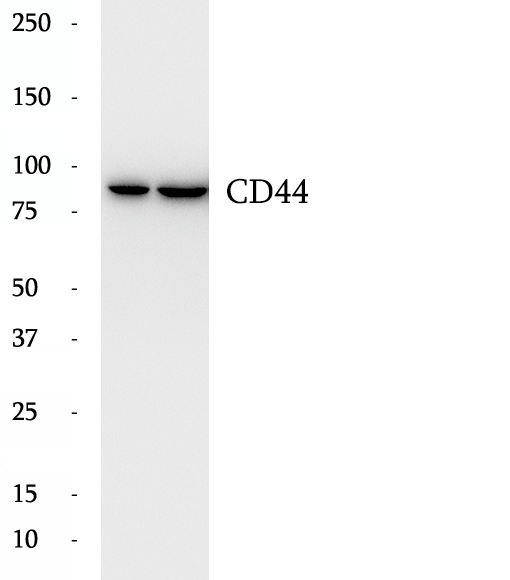
BP60793
|
Anti-CD44 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
CD44 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that mediates cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions through its affinity for hyaluronic acid (HA) and possibly also through its affinity for other ligands. Adhesion with HA plays an important role in cell migration, tumor growth and progression. CD44 is also involved in lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, and in hematopoiesis. This protein exists in multiple forms (with molecular weight ranging from 16 kDa to over 200 kDa) generated by alternative RNA splicing and extensive post-translational modifications.
|
|
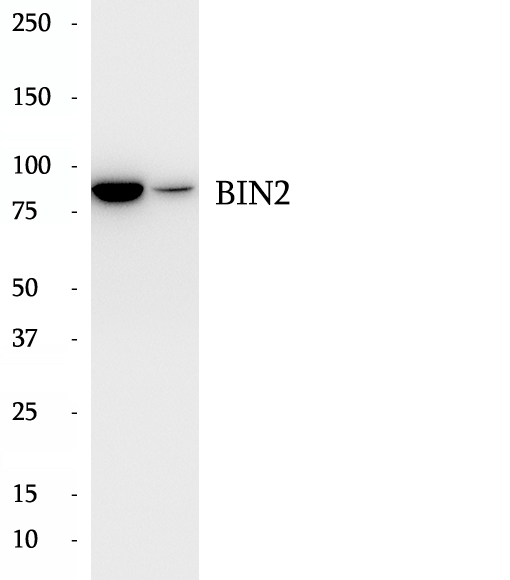
BP60480
|
Anti-BIN2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
BAR proteins, which are characterized by a common N-terminal BAR domain, are a family of adaptor proteins implicated in a diverse set of cellular processes. BIN1 (bridging integrator 1) and BIN2 are BAR proteins. The human BIN2 gene is located at chromosome 4q22.1, and encodes a 565-amino acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of ~62 kDa. It shows preferential expression in hematopoietic tissues, with highest mRNA levels in spleen and peripheral blood leukocytes and also high levels in thymus, colon, and placenta. BIN2 has been shown to migrate with an apparent mobility of ~80 kDa, and interact with BIN1.
|
|
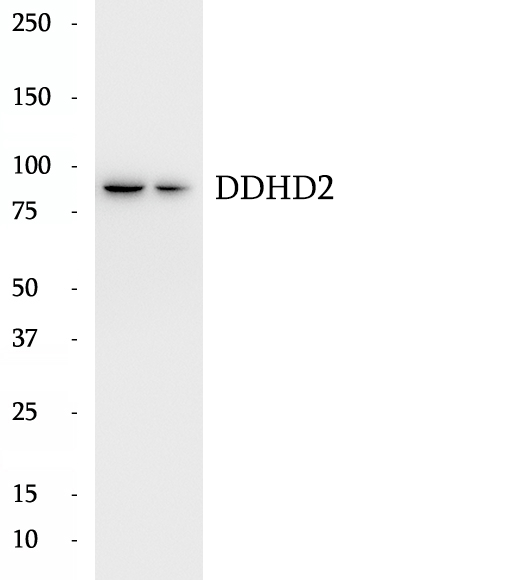
BP61271
|
Anti-DDHD2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DDHD2, also known as KIAA0725p, is a member of the intracellular phospholipase A1 (PLA1) protein family which comprises a group of enzymes that hydrolyze the sn-1 ester bond of phospholipids, producing 2-acyl-lysophospholipids and fatty acids. DDHD2 prefers phosphatidic acid as substrate and has a role in efficient membrane trafficking from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane. The gene of DDHD2 maps to chromosome 8p11.23, and encodes a 711-amino-acid protein with a calculated molecular mass of 81 kDa. It has been reported that DDHD2 immunoblot analysis of various tissue extracts revealed two bands of 90 and 85 kDa.
|
|
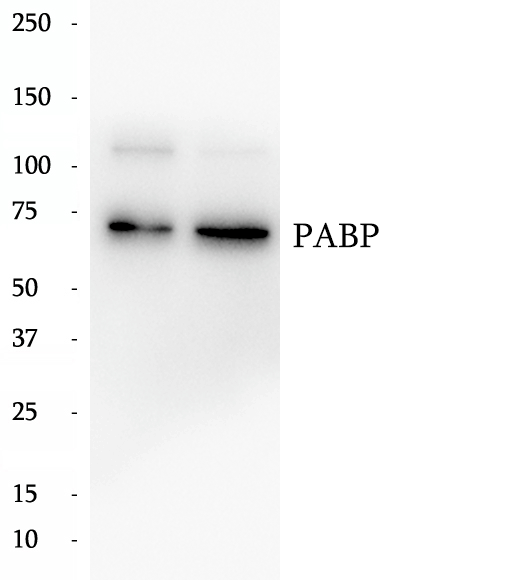
BP63373
|
Anti-PABP antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The poly (A)-binding protein (PABP), which is found complexed to the 3-prime poly (A) tail of eukaryotic mRNA, is required for poly (A) shortening and translation initiation. Polyadenylate-binding protein 1 (PABPC1) is a cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling protein important for protein translation initiation, and both RNA processing and stability. In the cytoplasm, PABPC1 binds to the 3' poly (A) tail of eukaryotic mRNAs through its RNA-recognition motifs (RRM) and interacts with the N-terminus of eIF4G, part of the eIF4F complex associated with the 5' cap structure.
|
|
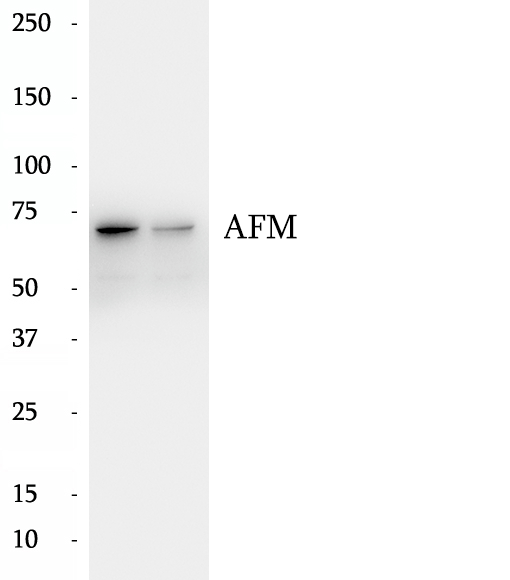
BP60095
|
Anti-AFM antibody
|
|
|
|
|
AFM (Afamin) is a member of the albumin superfamily, which comprises albumin, vitamin D-binding protein, a-fetoprotein, and afamin. AFM is present in the plasma/serum, cerebrospinal fluid, and follicular fluid, and functions as a vitamin E-binding protein. Alterations of expression level of AFM have been linked to variety of diseases like cancer.
|