|
BP62997
|
Anti-MYH2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MYH2 (Myosin II) is a member of the class II or conventional myosin heavy chains. Myosin II was first isolated from muscle but is also found in non muscle cells, and it is especially enriched in highly motile cell types such as amoebae. It forms bipolar filaments that interact with actin filaments to produce contraction. And it is the motor protein that generates force to drive muscle contraction. Functions in skeletal muscle contraction. The antibody is specific to MYH2, will not bind other myosins. It is a skeletal muscle specific antibody.
|
|
BP63013
|
Anti-MYO5B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MYO5B is a member of the class V of unconventional, dimeric nonfilamentous myosins, which may be involved in vesicular trafficking. Members of the Rab family of small GTPases, consisting of Rab11a, Rab11b, and Rab25, have recently emerged as potential mediators of vesicle transport by MYO5B. MYO5B is required for polarization of hepatocytes and mutations of MYO5B could disrupt epithelial cell polarity. Loss-of-Function of MYO5B caused by mutation is the main cause of microvillus inclusion disease (MVID). Recently it was reported that the expression of MYO5B was downregulated in gastric cancer and inactivation of MYO5B may contribute to tumorigenesis.
|
|
BP63736
|
Anti-PNO1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The function of PNO1 remains largely unknown in mammal. PNO1 plays a role in proteasome and ribosome neogenesis in yeast.
|
|
BP62203
|
Anti-HO-1/HMOX1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Heme oxygenase (HMOX1) catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the degradation of heme to yield equimolar quantities of biliverdin Ixa, carbon monoxide (CO), and iron. It has 3 isoforms: HO-1 is highly inducible, whereas HO-2 and HO-3 are constitutively expressed is expressed in many tissues and vascular smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells and has been identified as an important endogenous protective factor induced in many cell types by various stimulants, such as hemolysis, infiammatory cytokines,oxidative stress, heat shock, heavy metals, and endotoxin (James R. Reed, Pharmacology, 535-568).
|
|
BP61780
|
Anti-FOXO1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
FOXO1, also named as FOXO1A, FKHR and FKH1, is a member of the FOXO subfamily of Forkhead transcription factors. FOXO1is a transcription factor which acts as a regulator of cell responses to oxidative stress. FOXO1 interacts with LRPPRC andSIRT1. In the presence of KIRT1, FOXO1 mediates down-regulation of cyclin D1 and up-regulation of CDKN1B levels which are required for cell transition from proliferative growth to quiescence. FOXO1 contains three predicted protein kinase B phosphorylation sites (Thr-24, Ser-256, and Ser-319) that are conserved in other FOXO proteins. The t (2;13) and the variant t (1;13) translocations generate PAX3/FKHR and PAX7/FKHR fusion proteins respectively. The resulting protein is a transcriptional activator. Defects in FOXO1 are a cause of rhabdomyosarcoma type 2 (RMS2).
|
|
BP62426
|
Anti-ISG15 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ISG15 is a ubiquitin-like protein that becomes conjugated to many cellular proteins upon activation by interferon-alpha (IFNA) and -beta (IFNB). ISG15 forms covalent conjugates with its target proteins in a process called ISGylation, which in mammals is known to play a role in antiviral immunity. ISG15 proteins possess two ubiquitin-like (UBL) domains and a highly conserved C-terminal LRGG sequence, the latter being known as the ubiquitin conjugation motif. Intracellular ISG15 are conjugated, via the LRGG motif, to target proteins through a process called ISGylation, which resembles largely ubiquitination, the process of formation of ubiquitin conjugates. Unconjugated extracellular ISG15, which are released from several types of human and murine cells, are known to possess cytokine-like activity.
|
|
BP64211
|
Anti-RPS25 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Ribosomal protein S25 (RPS25) is a novel MDM2 interacting protein. It may be involved in viral replication of Dicistroviridae and hepatitis C viruses. RPS25 is overexpressed in human leukemia cells exhibiting adriamycin resistance. It may have a role in p53-mediated apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest. The expected MW of RPS25 is about 15-17kDa. Catalog# 23599-1-AP is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against full-length RPS25, and is recommended for ELISA, Western blotting.
|
|
BP65398
|
Anti-ZNF22 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ZNF22 encodes a protein that is expressed in the epithelial component of the developing tooth organ during early bud and cap stages as well as in osteoblasts of craniofacial bone and the developing tongue.
|
|
BP64632
|
Anti-SSBP1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSBP1 gene.
|
|
BP62343
|
Anti-IL-11RA antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Interleukin-11 (IL-11), a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines, was firstly identified in bone marrow-derived stromal cells and gp130. IL-11RA binds IL-11 and gp130 transmits signals to the nucleus via Janus kinase (JAK) activation. In addition to a membrane-bound form, IL-11RA can also exist as a soluble form (sIL-11RA) that acts as an agonist of IL-11 activity.
|
|
BP62654
|
Anti-LRG1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
LRG1, also known as LRG, is a member of the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) family of proteins, containing eight LRR (leucine-rich) repeats and one LRRCT domain. The gene of LRG1 maps to chromosome 19p13.3, and encodes a 347-amino acid protein with a predicted unmodified molecular weight of 38 kD. The mature form of LRG1 is a secreted glycoprotein which has 312 amino acids and an experimentally determined molecular mass of 45 kD. The LRR family of proteins, including LRG1, have been shown to be involved in protein-protein interaction, signal transduction, and cell adhesion and development. LRG1 is expressed during granulocyte differentiation. Levels of the LRG protein are markedly elevated in acute appendicitis and therefore could be used as a diagnostic aid.
|
|
BP64534
|
Anti-SNX17 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Sorting nexin 17 (SNX17, synonym: KIAA0064) is a member of the sorting nexin family. Members of this family contain a phox (PX) domain, which is a phosphoinositide binding domain, and are involved in intracellular trafficking.SNX17 does not contain a coiled coil region, like some family members, but contains a B41 domain. This protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin, and may function in the intracellular trafficking of P-selectin.
|
|
BP62547
|
Anti-KRT34 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Keratins are a large family of proteins that form the intermediate filament cytoskeleton of epithelial cells. Keratin expression is highly regulated, tissue specific, and varies according to cell-state. Type I keratins consist of acidic, low molecular weight proteins with MW ranging from 40 kDa (KRT19) to 64 kDa (KRT9). Type 2 keratins consist of basic or neutral, high molecular weight proteinswith MW from 52 kDa (KRT8) to 67 kDa (KRT18). KRT 34 is a type I keratin.
|
|
BP62018
|
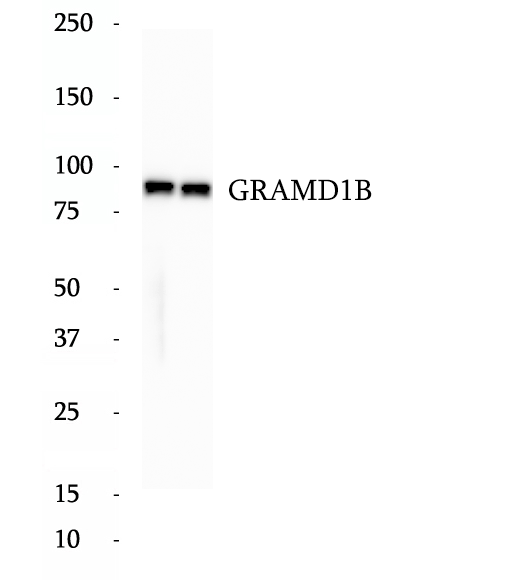
Anti-GRAMD1B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
GRAMD1B, also named as KIAA1201, contains a transmembrane region and two domains of known function; the GRAM domain and a VASt domain. It is predicted to localize in the nucleus, supported by several nuclear transport signals and nuclearly associated motifs. This highly conserved gene is found in a variety of vertebrates and invertebrates, however, it is not found in bacteria or fungi. There're some isoforms with MW 50 kDa and 81-87 kDa. With phosphor modification, it's about 90-110 kDa in WB detection.
|
|
BP62207
|
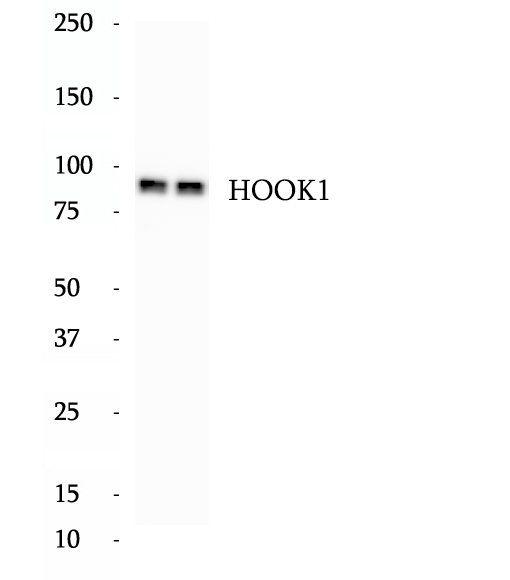
Anti-HOOK1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
HOOK1, an orthologue of the Drosophila Hook protein, is a member of the microtubule-binding HOOK family of cytosolic coiled-coil proteins (HOOK1, HOOK2, HOOK3). These proteins contain conserved N-terminal domains, which attach to microtubules, and more divergent C-terminal domains, which mediate binding to organelles. HOOK1 is required for spermatid differentiation. It is probably involved in the positioning of the microtubules of the manchette and the flagellum in relation to the membrane skeleton. HOOK1 is a component of the FTS/Hook/FHIP complex which functions to promote vesicle trafficking and/or fusion via the HOPS (homotypic vesicular protein sorting) complex.
|
|
BP61390
|
Anti-DOCK4 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DOCK4, originally identified as a product of a gene which is deleted during tumor progression, is a member of DOCK180 family proteins. Dock4 has been found recently to be associated with several neuropsychiatric diseases, including autism, dyslexia, and schizophrenia. Multiple studies in fibroblasts then confirmed that Dock4 is capable of controlling cell migration by transducing several upstream signals, such as Wnt, platelet-derived growth factor, and RhoG, toward activation of Rac1. Mutations in this gene have been associated with ovarian, prostate, glioma, and colorectal cancers.
|
|
BP61103
|
Anti-CRIPT antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The clustering and immobilization of receptors and ion channels located at specific subcellular sites are believed to be mediated by intracellular proteins that attach these membrane proteins to the cytoskeleton. Receptors and ion channels interact with cytoplasmic proteins, which involved in the modulation or downstream signaling mechanisms of the receptor/ion channel. CRIPT is the protein that binds to the third PDZ (PDZ3) domain of PSD95, which binds to and clusters a variety of membrane proteins, including Shaker-type potassium channel subunits and NMDA receptor NR2 subunits, via its first 2 N-terminal PDZ domains
|
|
BP61252
|
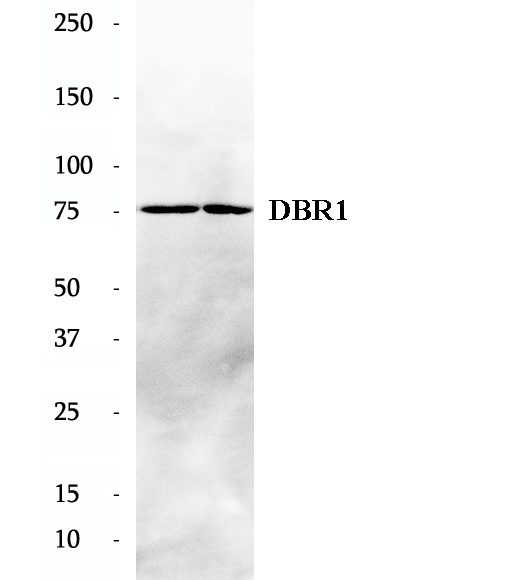
Anti-DBR1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DBR1 (Lariat debranching enzyme) hydrolyzes 2-prime-to-5-prime branched phosphodiester bonds at the branch point of excised lariat intron RNA and converts them into linear molecules. DBR1 belongs to the lariat debranching enzyme family. Inhibiton of Dbr1 can suppress TDP-43 toxicity in primary neurons, suggesting that Dbr1 could be a potential therapeutic target for ALS and related TDP-43 proteinopathies. This protein has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP65083
|
Anti-TXNL4B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Dim2, also known as TXNL4B (thioredoxin-like 4B), or DLP, is a 149 amino acid nuclear protein that exists as a homodimer and plays an essential role in pre-mRNA splicing. Evolutionarily related and sharing 38% sequence identity with Dim1, Dim2 is required for S/G(2) transition during the cell cycle and is able to bind the PRP6 (U5-102K) subunit of the spliceosome. The gene encoding Dim2 maps to human chromosome 16, which encodes over 900 genes and comprises nearly 3% of the human genome. The rare disorder Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome is associated with chromosome 16, as is Crohn's disease, which is a gastrointestinal inflammatory condition.
|
|
BP64446
|
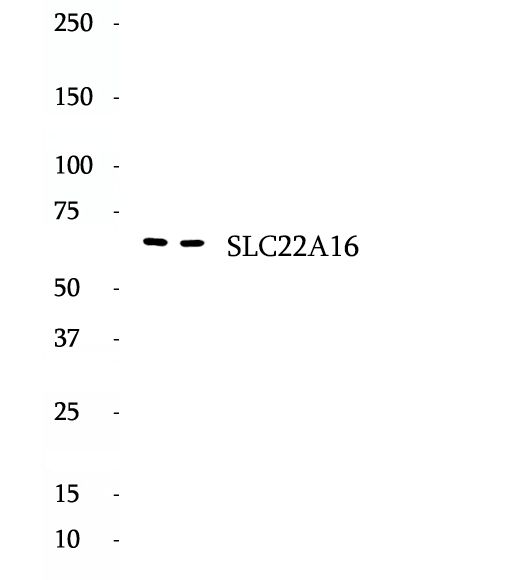
Anti-SLC22A16 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SLC22A16, also named as CT2, FLIPT2, or OCT6, belongs to the major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily and organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family. SLC22A16 encodes an organic zwitterion transporter protein that transports carnitine and some anticancer drugs, including anthracyclines. As a carnitine transporter, SLC22A16 is involved in the regulation of fatty acid oxidation (FAO), which plays an important role also in the metabolic transformation of cancer cells. SLC22A16 expression in cancer cells is associated with increased sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin. SLC22A16 has 3 isoforms with the molecular mass of 58, 61 and 65 kDa.
|