|
BP63453
|
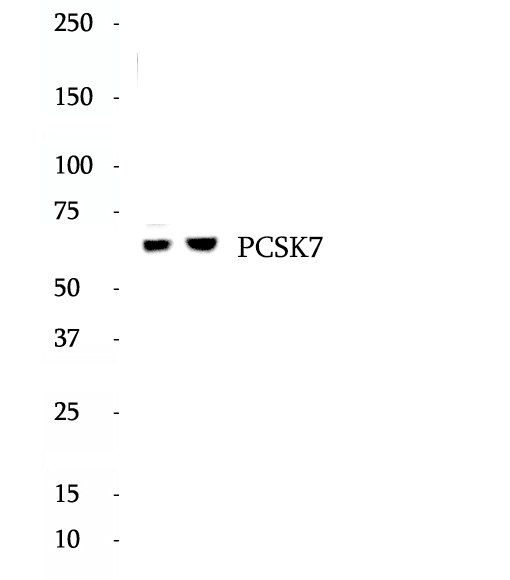
Anti-PCSK7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK7 gene. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family. The members of this family are proprotein convertases that process latent precursor proteins into their biologically active products. This encoded protein is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease. It is structurally related to its family members, PACE and PACE4. This protein is concentrated in the trans-Golgi network, associated with the membranes, and is not secreted. It can process proalbumin and is thought to be responsible for the activation of HIV envelope glycoproteins gp160 and gp140.
|
|
BP60272
|
Anti-ARC antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ARC, also named as KIAA0278 and Arg3.1, mediates endocytosis of neuronal AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs). It is required for consolidation of synaptic plasticity as well as formation of long-term memory. ARC plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. It is required in the stress fiber dynamics and cell migration.
|
|
BP65244
|
Anti-VIRMA/KIAA1429 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
VIRMA (KIAA1429) is a key component of m6A methyltransferase (writer) complex that include METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, VIRMA, HAKAI, ZC3H13, and RBM15. VIRMA mediates methylation in the 3'UTR and around the stop codon, thus affecting alternative polyadenylation. VIRMA has been reported to act as oncogenic factor in breast cancer and liver cancer.
|
|
BP61403
|
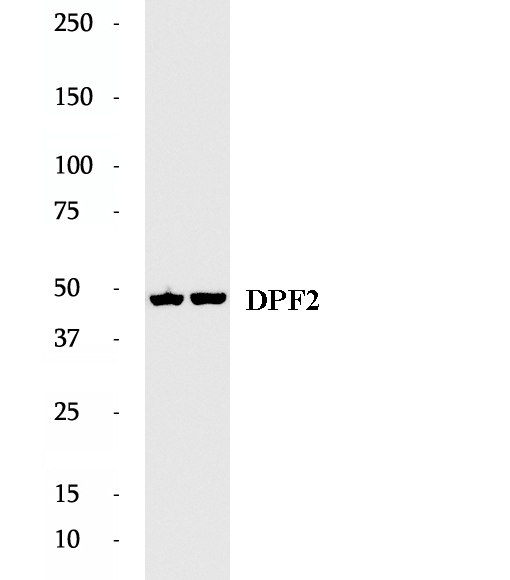
Anti-DPF2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DPF2, also named as BAF45D or UBID4, is a 391 amino acid protein, which belongs to the requiem/DPF family. DPF2 may be a transcription factor required for the apoptosis response following survival factor withdrawal from myeloid cells and might also have a role in the development and maturation of lymphoid cells. DPF2 was recently shown to inhibit the myeloid differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor and acute myelogenous leukemia cells.
|
|
BP62811
|
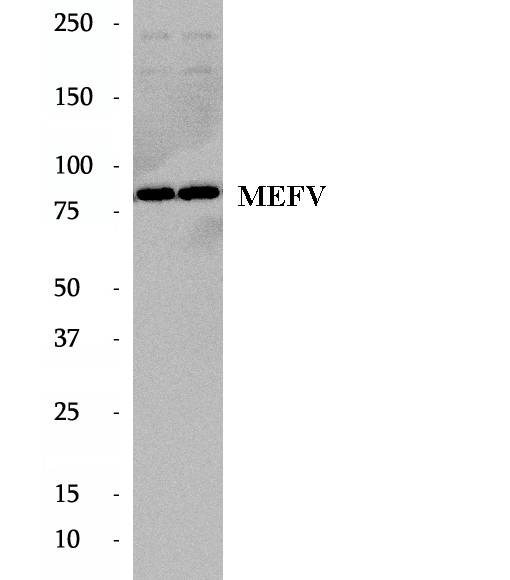
Anti-MEFV antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MEFV, a gene encoding a protein of unknown function, is the genetic cause of Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), a recessively inherited disorder characterized by recurring attacks of fever and serositis. Recently mutation of MEFV has been reported to cause autoinflammatory disease distinct from FMF.
|
|
BP65192
|
Anti-USP32 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
USP32 belongs to the peptidase C19 family. USP32 catalytic the reaction:Ubiquitin C-terminal thioester + H2O = ubiquitin + a thiol.
|
|
BP64503
|
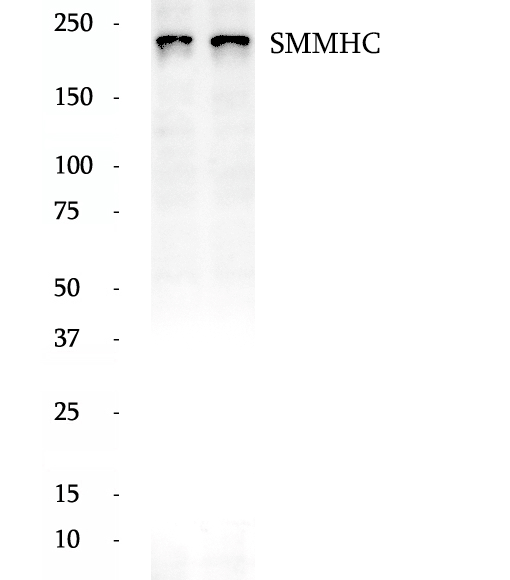
Anti-SMMHC antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SMMHC (smooth muscle myosin heavy chain; MYH11) is a contractile protein of smooth muscle cells. It is specifically expressed in cells derived from smooth muscle lineages. SMMHC is used as vascular smooth muscle cell (vSMC) contractile marker. It is also an excellent marker for myoepithelial cells, with no or few cross-reaction with myofibroblasts, thus very useful in the evaluation of stromal invasion.
|
|
BP65232
|
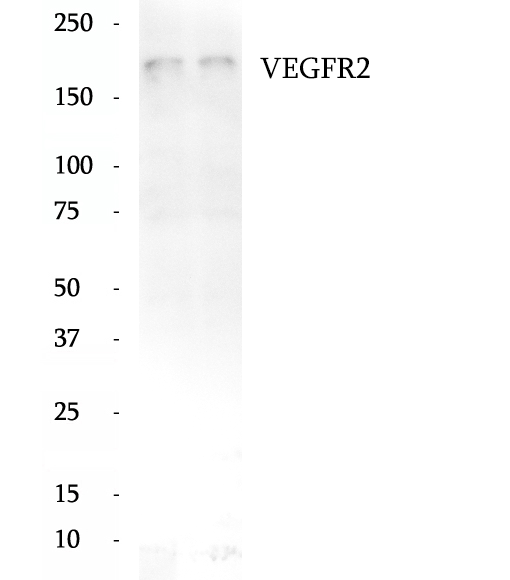
Anti-VEGFR2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
KDR, also named as VEGFR-2, FLK1 and CD309, is a receptor for VEGF or VEGFC. KDR which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. The VEGF-kinase ligand/receptor signaling system plays a key role in vascular development and regulation of vascular permeability. In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. KDR functions as the main mediator of VEGF-induced endothelial proliferation, survival, migration, tubular morphogenesis and sprouting. Mutations of this gene are implicated in infantile capillary hemangiomas.
|
|
BP60192
|
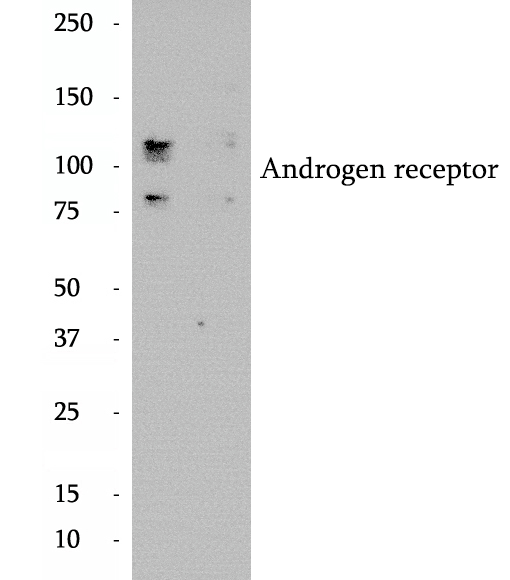
Anti-Androgen receptor antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.
|
|
BP61814
|
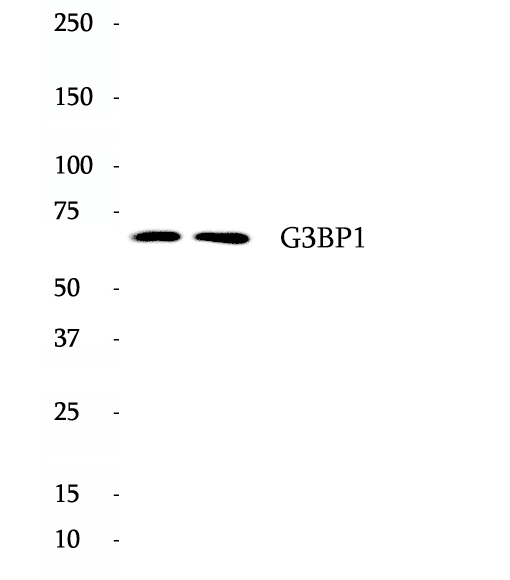
Anti-G3BP1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the G3BP1 gene. This gene encodes one of the DNA-unwinding enzymes which prefers partially unwound 3'-tailed substrates and can also unwind partial RNA/DNA and RNA/RNA duplexes in an ATP-dependent fashion. This enzyme is a member of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-binding proteins and is also an element of the Ras signal transduction pathway. It was originally reported to bind specifically to the Ras-GTPase-activating protein by associating with its SH3 domain, but this interaction has recently been challenged. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined.
|
|
BP64269
|
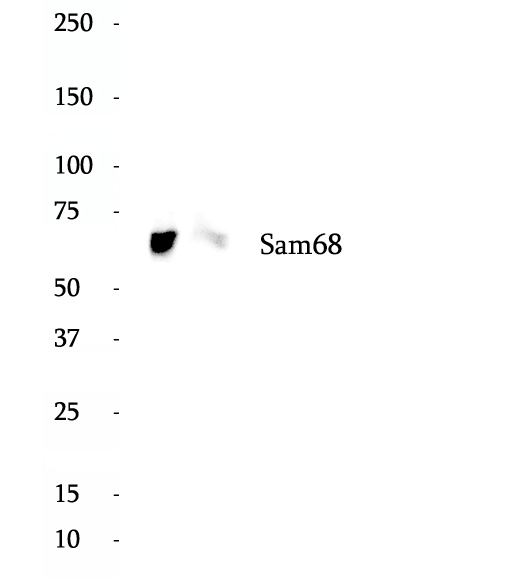
Anti-Sam68 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
KH domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KHDRBS1 gene. This gene encodes a member of the K homology domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein family. The encoded protein appears to have many functions and may be involved in a variety of cellular processes, including alternative splicing, cell cycle regulation, RNA 3'-end formation, tumorigenesis, and regulation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression.
|
|
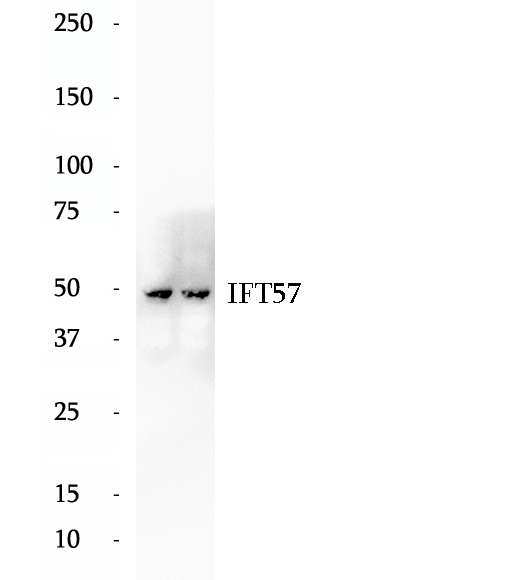
BP62311
|
Anti-IFT57 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
IFT57, also named as DERP8, ESRRBL1, HIPPI and MHS4R2, belongs to the IFT57 family. It is required for the formation of cilia. IFT57 plays an indirect role in sonic hedgehog signaling, cilia being required for all activity of the hedgehog pathway. It is a component of IFT complex B which composed of IFT88, IFT57, TRAF3IP1, IFT52, IFT27, HSPB11 and IFT20. In contrast to BBS proteins, IFT57 and IFT88 is found in almost every cilium.
|
|
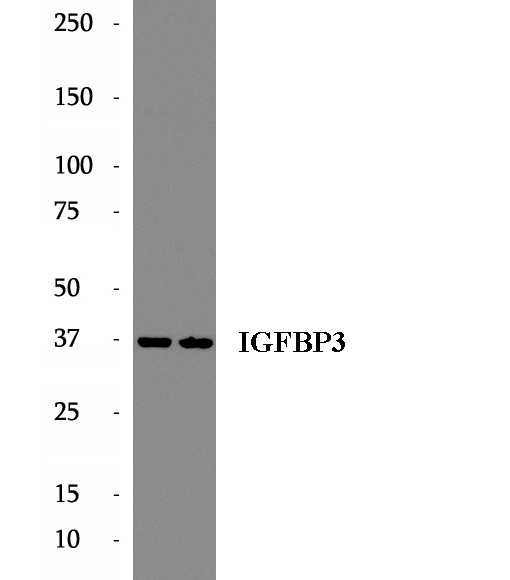
BP62322
|
Anti-IGFBP3 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) contains a 27 amino acid putative signal sequence followed by a mature protein of 264 amino acids with 18 cysteine residues clustered near the N- and C-terminus. Accordingly, expression of the cloned IGFBP-3 cDNA in mammalian tissue culture cells results in secretion of the protein into the culture medium.IGFBP-3 shares high homology (33% amino acid identity) including conservation of all 18 cysteine residues with a smaller human IGF-binding protein (BP-28) identified in amniotic fluid. IGFBP-3 has one or more glycosylation sites with a protein core of ∼30 kDa. Western blots revealed that the 39-45 kDa IGFBP-3 fragment is a glycoprotein.
|
|
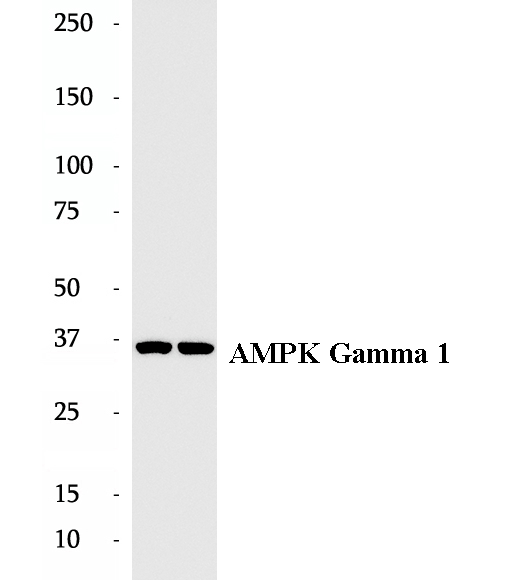
BP60187
|
Anti-AMPK Gamma 1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 1 non-catalytic subunit (PRKAG1, synonyms: AMPKG, MGC8666) is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic and subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and iAMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a highly conserved heterotrimeric serine/threonine kinase widely characterised as a sensor of cellular energetic stress. AMPK is a heterotrimeric complex consisting of a catalytic α-subunit and two regulatory subunits (β and γ). AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. AMPK gamma 1 is one of the gamma regulatory subunits of AMPK.
|
|
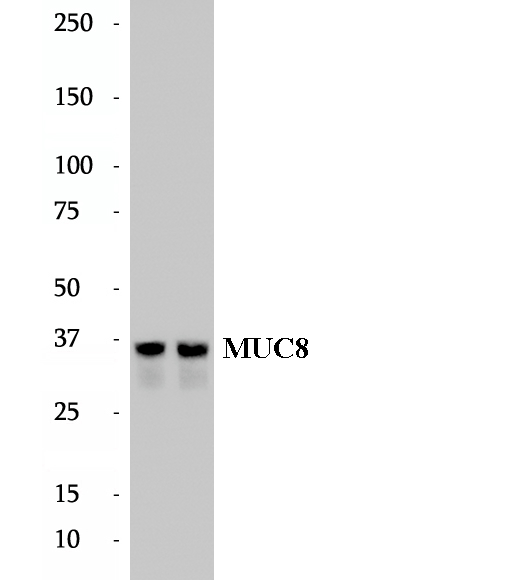
BP62970
|
Anti-MUC8 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Mucin glycoproteins (Mucins) are major constituents of the glycocalyx that covers mucosal epithelium. MUC8 is one of the major mucins in the ethmoid mucosa and is upregulated by chronic inflammation. TNFa, IL-1b and a combination of both can significantly increase Mucin 8 mRNA levels, suggesting that a mixture of inflammatory mediators can synergistically increase secretion of mucin in human nasal epithelium. This antibody is specific to MUC8.
|
|
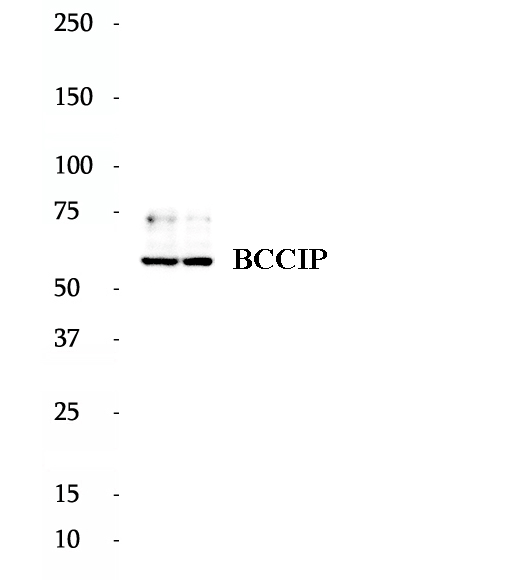
BP60447
|
Anti-BCCIP antibody
|
|
|
|
|
BCCIP (or TOK1) is isolated as a BRCA2- and CDKN1A (p21)-interacting protein and is implicated in homologous recombination (HR) pathway and inhibition of DNA replication stress. BCCIP is an evolutionarily conserved nuclear protein with multiple interacting domains. BCCIP deficiency in mice impaired embryonic and postnatal neural development, causing severe ataxia, cerebral and cerebellar defects, and microcephaly, which are associated with spontaneous DNA damage and subsequent cell death in the proliferative cell populations of the neural system during embryogenesis. BCCIP is essential for maintaining the transactivation activity of wild type p53 suggesting a potential role of BCCIP in cancer etiology.
|
|
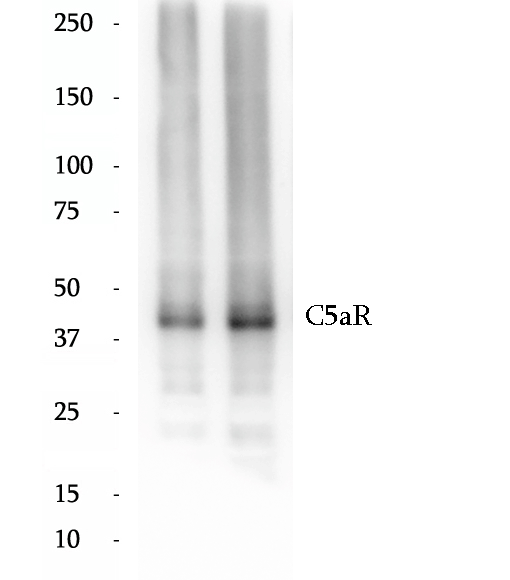
BP60586
|
Anti-C5aR antibody
|
|
|
|
|
C5aR, also named as CD88, is a G protein-coupled receptor for the anaphylatoxin C5a, a cleavage product of the complement cascade. The C5a ligand is a proinflammatory component of host defense. C5aR is activated upon binding of the C5a molecule. Receptor activation stimulates chemotaxis, granule enzyme release, intracellular calcium release and superoxide anion production. The deduced sequence of C5aR contains 350 amino acids, giving a calculated molecular weight of 39 kDa. C5aR has an N-linked glycosylation site in the N-terminal extracellular domain. The apparent molecular weight of C5aR is about 40-52 kDa.
|
|
BP62558
|
Anti-L2HGDH antibody
|
|
|
|
|
L2HGDH (L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial) is also named as duranin, C14orf160 and belongs to the L2HGDH family. The putative L2HGDH is predicted to be targeted to the mitochondria where its mitochondrial targeting sequence is presumably removed. Defects in L2HGDH are the cause of L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (L2HGA). It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 50 kDa and 48 kDa. L2HGDH also can be detected as ~45kD due to the 51aa transit peptide cleaved.
|
|
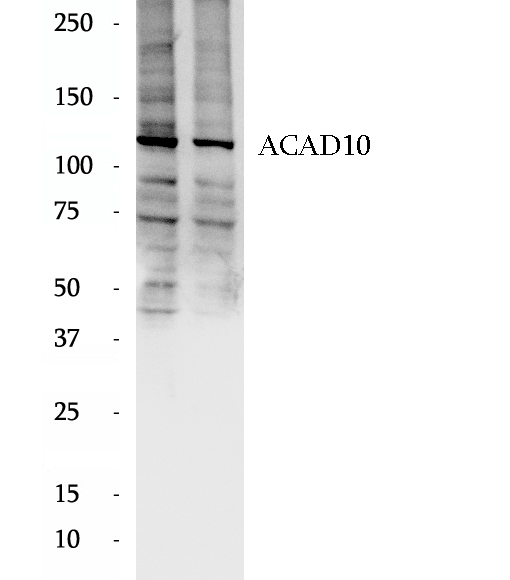
BP60021
|
Anti-ACAD10 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ACAD10 (Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 10) belongs to the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family. ACAD10 has significant activity towards the branched-chain substrates R and S, 2 methyl-C15-CoA and is highly expressed in fetal but not adult brain. This pattern of expression is similar to that of LCAD, another ACAD previously shown to be involved in long branched chain fatty acid metabolism. It has 4 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
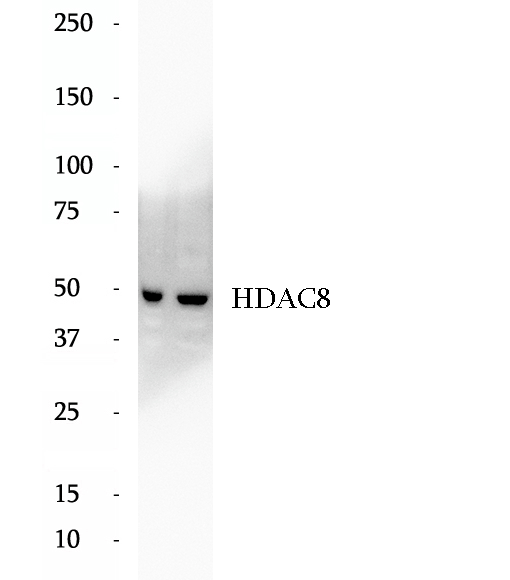
BP62113
|
Anti-HDAC8 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin. At least 4 classes of HDAC were identified. As a class I HDAC, HDAC 8 was primarily found in the nucleus. It catalyzes the deacetylation of lysine residues in the histone N-terminal tails and represses transcription in large multiprotein complexes with transcriptional co-repressors. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against full length HDAC8 of human origin.
|