|
BP62018
|
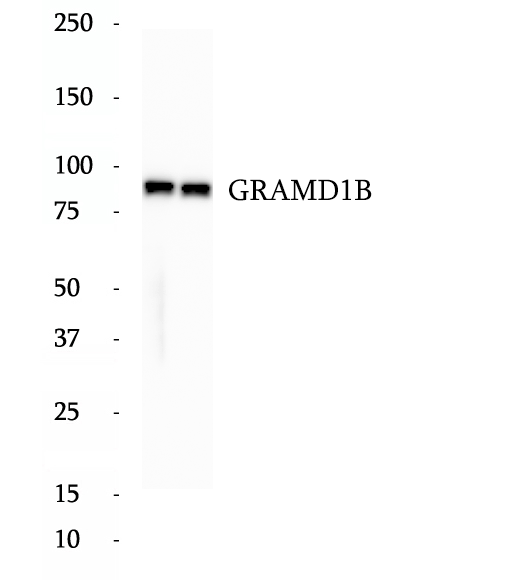
Anti-GRAMD1B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
GRAMD1B, also named as KIAA1201, contains a transmembrane region and two domains of known function; the GRAM domain and a VASt domain. It is predicted to localize in the nucleus, supported by several nuclear transport signals and nuclearly associated motifs. This highly conserved gene is found in a variety of vertebrates and invertebrates, however, it is not found in bacteria or fungi. There're some isoforms with MW 50 kDa and 81-87 kDa. With phosphor modification, it's about 90-110 kDa in WB detection.
|
|
BP62207
|
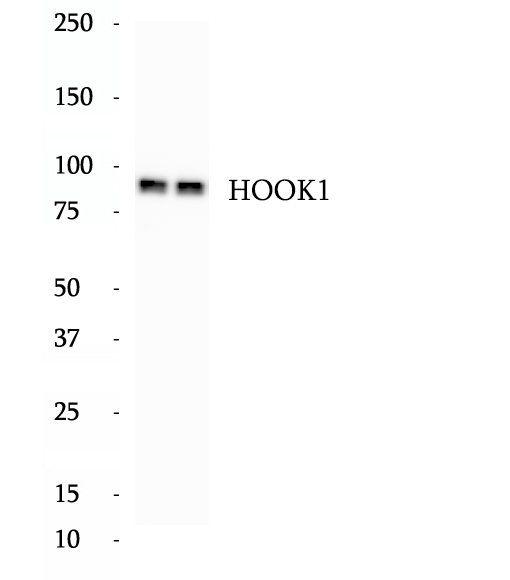
Anti-HOOK1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
HOOK1, an orthologue of the Drosophila Hook protein, is a member of the microtubule-binding HOOK family of cytosolic coiled-coil proteins (HOOK1, HOOK2, HOOK3). These proteins contain conserved N-terminal domains, which attach to microtubules, and more divergent C-terminal domains, which mediate binding to organelles. HOOK1 is required for spermatid differentiation. It is probably involved in the positioning of the microtubules of the manchette and the flagellum in relation to the membrane skeleton. HOOK1 is a component of the FTS/Hook/FHIP complex which functions to promote vesicle trafficking and/or fusion via the HOPS (homotypic vesicular protein sorting) complex.
|
|
BP61390
|
Anti-DOCK4 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DOCK4, originally identified as a product of a gene which is deleted during tumor progression, is a member of DOCK180 family proteins. Dock4 has been found recently to be associated with several neuropsychiatric diseases, including autism, dyslexia, and schizophrenia. Multiple studies in fibroblasts then confirmed that Dock4 is capable of controlling cell migration by transducing several upstream signals, such as Wnt, platelet-derived growth factor, and RhoG, toward activation of Rac1. Mutations in this gene have been associated with ovarian, prostate, glioma, and colorectal cancers.
|
|
BP61103
|
Anti-CRIPT antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The clustering and immobilization of receptors and ion channels located at specific subcellular sites are believed to be mediated by intracellular proteins that attach these membrane proteins to the cytoskeleton. Receptors and ion channels interact with cytoplasmic proteins, which involved in the modulation or downstream signaling mechanisms of the receptor/ion channel. CRIPT is the protein that binds to the third PDZ (PDZ3) domain of PSD95, which binds to and clusters a variety of membrane proteins, including Shaker-type potassium channel subunits and NMDA receptor NR2 subunits, via its first 2 N-terminal PDZ domains
|
|
BP61252
|
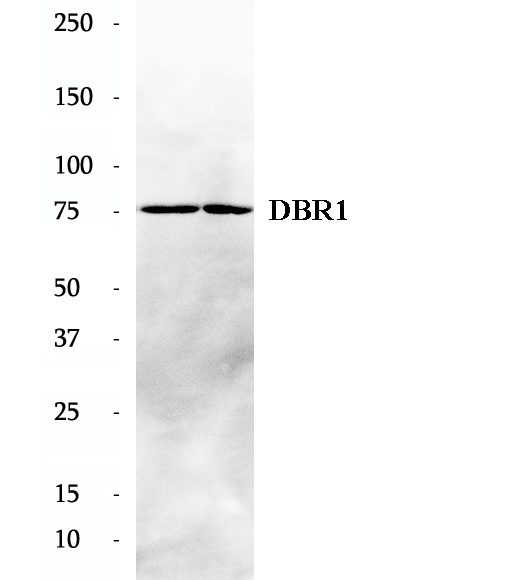
Anti-DBR1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DBR1 (Lariat debranching enzyme) hydrolyzes 2-prime-to-5-prime branched phosphodiester bonds at the branch point of excised lariat intron RNA and converts them into linear molecules. DBR1 belongs to the lariat debranching enzyme family. Inhibiton of Dbr1 can suppress TDP-43 toxicity in primary neurons, suggesting that Dbr1 could be a potential therapeutic target for ALS and related TDP-43 proteinopathies. This protein has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP65083
|
Anti-TXNL4B antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Dim2, also known as TXNL4B (thioredoxin-like 4B), or DLP, is a 149 amino acid nuclear protein that exists as a homodimer and plays an essential role in pre-mRNA splicing. Evolutionarily related and sharing 38% sequence identity with Dim1, Dim2 is required for S/G(2) transition during the cell cycle and is able to bind the PRP6 (U5-102K) subunit of the spliceosome. The gene encoding Dim2 maps to human chromosome 16, which encodes over 900 genes and comprises nearly 3% of the human genome. The rare disorder Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome is associated with chromosome 16, as is Crohn's disease, which is a gastrointestinal inflammatory condition.
|
|
BP64446
|
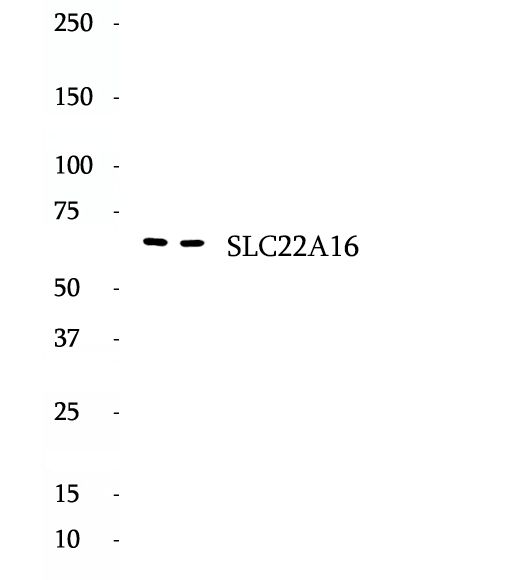
Anti-SLC22A16 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SLC22A16, also named as CT2, FLIPT2, or OCT6, belongs to the major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily and organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family. SLC22A16 encodes an organic zwitterion transporter protein that transports carnitine and some anticancer drugs, including anthracyclines. As a carnitine transporter, SLC22A16 is involved in the regulation of fatty acid oxidation (FAO), which plays an important role also in the metabolic transformation of cancer cells. SLC22A16 expression in cancer cells is associated with increased sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin. SLC22A16 has 3 isoforms with the molecular mass of 58, 61 and 65 kDa.
|
|
BP63453
|
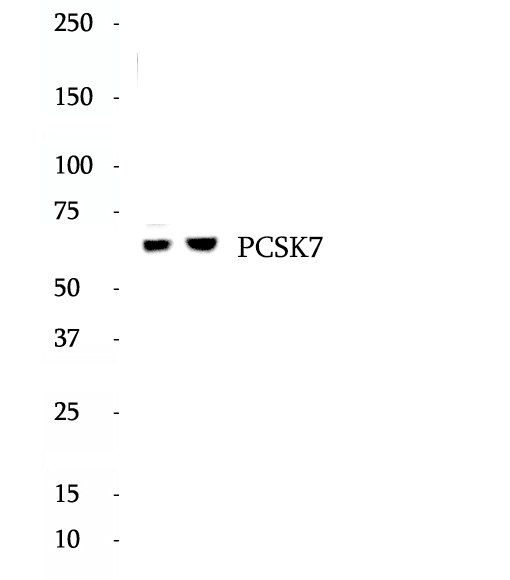
Anti-PCSK7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK7 gene. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family. The members of this family are proprotein convertases that process latent precursor proteins into their biologically active products. This encoded protein is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease. It is structurally related to its family members, PACE and PACE4. This protein is concentrated in the trans-Golgi network, associated with the membranes, and is not secreted. It can process proalbumin and is thought to be responsible for the activation of HIV envelope glycoproteins gp160 and gp140.
|
|
BP60272
|
Anti-ARC antibody
|
|
|
|
|
ARC, also named as KIAA0278 and Arg3.1, mediates endocytosis of neuronal AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs). It is required for consolidation of synaptic plasticity as well as formation of long-term memory. ARC plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. It is required in the stress fiber dynamics and cell migration.
|
|
BP65244
|
Anti-VIRMA/KIAA1429 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
VIRMA (KIAA1429) is a key component of m6A methyltransferase (writer) complex that include METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, VIRMA, HAKAI, ZC3H13, and RBM15. VIRMA mediates methylation in the 3'UTR and around the stop codon, thus affecting alternative polyadenylation. VIRMA has been reported to act as oncogenic factor in breast cancer and liver cancer.
|
|
BP61403
|
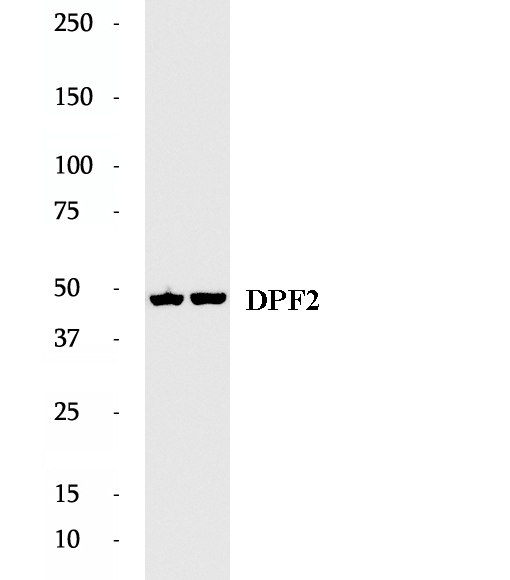
Anti-DPF2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DPF2, also named as BAF45D or UBID4, is a 391 amino acid protein, which belongs to the requiem/DPF family. DPF2 may be a transcription factor required for the apoptosis response following survival factor withdrawal from myeloid cells and might also have a role in the development and maturation of lymphoid cells. DPF2 was recently shown to inhibit the myeloid differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor and acute myelogenous leukemia cells.
|
|
BP62811
|
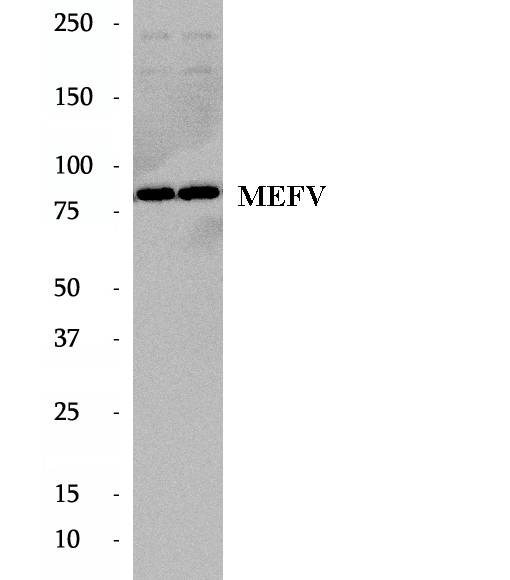
Anti-MEFV antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MEFV, a gene encoding a protein of unknown function, is the genetic cause of Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), a recessively inherited disorder characterized by recurring attacks of fever and serositis. Recently mutation of MEFV has been reported to cause autoinflammatory disease distinct from FMF.
|
|
BP65192
|
Anti-USP32 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
USP32 belongs to the peptidase C19 family. USP32 catalytic the reaction:Ubiquitin C-terminal thioester + H2O = ubiquitin + a thiol.
|
|
BP64503
|
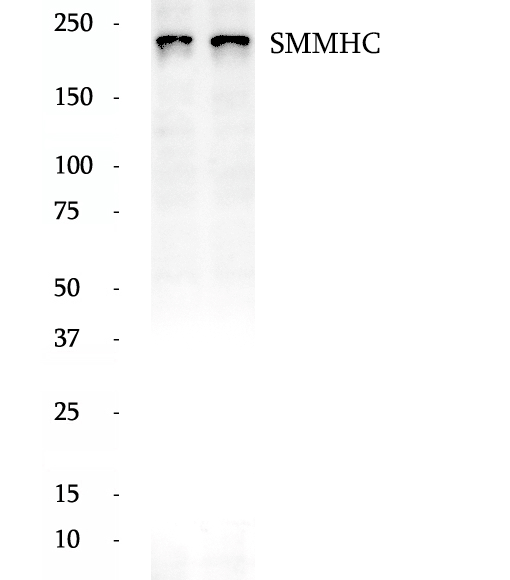
Anti-SMMHC antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SMMHC (smooth muscle myosin heavy chain; MYH11) is a contractile protein of smooth muscle cells. It is specifically expressed in cells derived from smooth muscle lineages. SMMHC is used as vascular smooth muscle cell (vSMC) contractile marker. It is also an excellent marker for myoepithelial cells, with no or few cross-reaction with myofibroblasts, thus very useful in the evaluation of stromal invasion.
|
|
BP65232
|
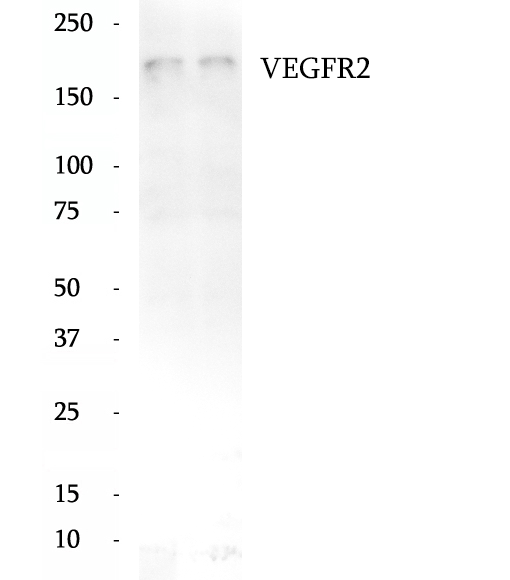
Anti-VEGFR2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
KDR, also named as VEGFR-2, FLK1 and CD309, is a receptor for VEGF or VEGFC. KDR which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. The VEGF-kinase ligand/receptor signaling system plays a key role in vascular development and regulation of vascular permeability. In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. KDR functions as the main mediator of VEGF-induced endothelial proliferation, survival, migration, tubular morphogenesis and sprouting. Mutations of this gene are implicated in infantile capillary hemangiomas.
|
|
BP60192
|
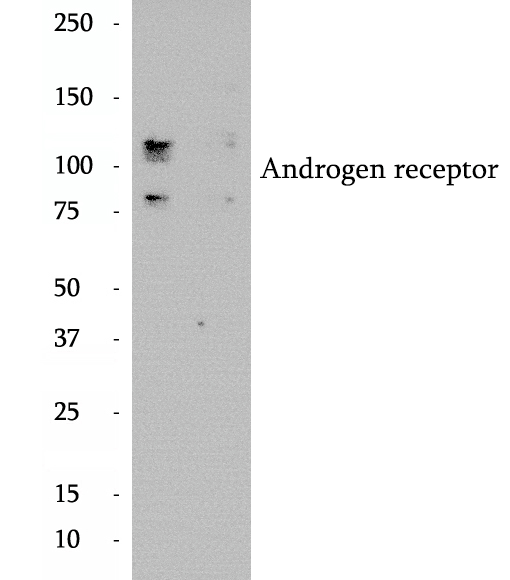
Anti-Androgen receptor antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.
|
|
BP61814
|
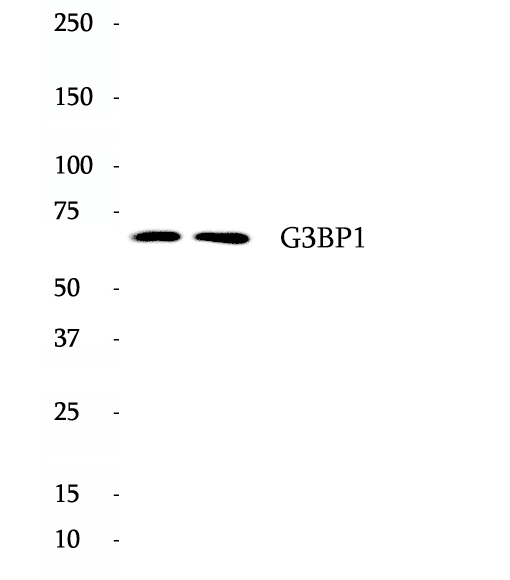
Anti-G3BP1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the G3BP1 gene. This gene encodes one of the DNA-unwinding enzymes which prefers partially unwound 3'-tailed substrates and can also unwind partial RNA/DNA and RNA/RNA duplexes in an ATP-dependent fashion. This enzyme is a member of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-binding proteins and is also an element of the Ras signal transduction pathway. It was originally reported to bind specifically to the Ras-GTPase-activating protein by associating with its SH3 domain, but this interaction has recently been challenged. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined.
|
|
BP64269
|
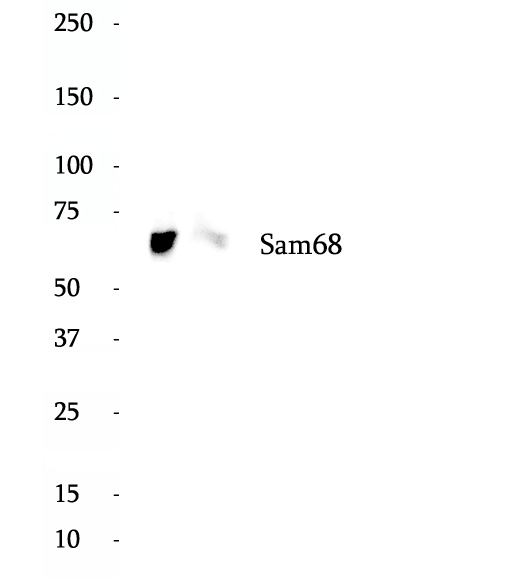
Anti-Sam68 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
KH domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KHDRBS1 gene. This gene encodes a member of the K homology domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein family. The encoded protein appears to have many functions and may be involved in a variety of cellular processes, including alternative splicing, cell cycle regulation, RNA 3'-end formation, tumorigenesis, and regulation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression.
|
|
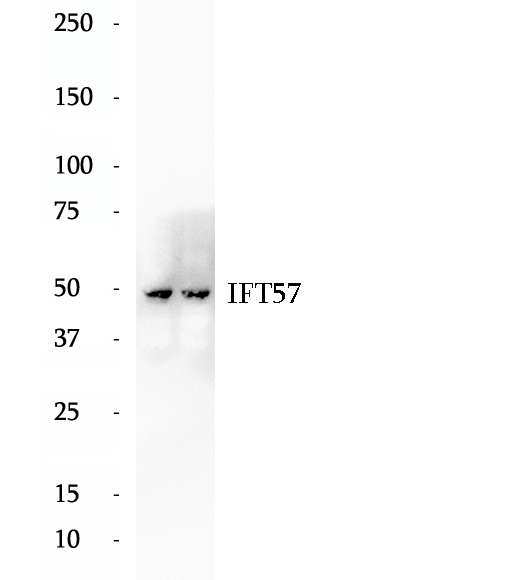
BP62311
|
Anti-IFT57 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
IFT57, also named as DERP8, ESRRBL1, HIPPI and MHS4R2, belongs to the IFT57 family. It is required for the formation of cilia. IFT57 plays an indirect role in sonic hedgehog signaling, cilia being required for all activity of the hedgehog pathway. It is a component of IFT complex B which composed of IFT88, IFT57, TRAF3IP1, IFT52, IFT27, HSPB11 and IFT20. In contrast to BBS proteins, IFT57 and IFT88 is found in almost every cilium.
|
|
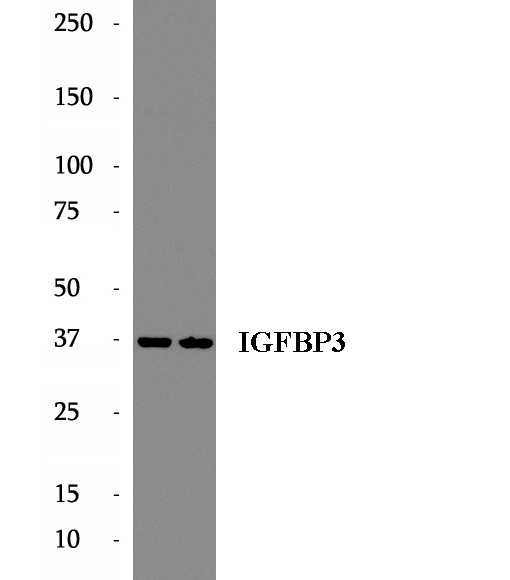
BP62322
|
Anti-IGFBP3 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) contains a 27 amino acid putative signal sequence followed by a mature protein of 264 amino acids with 18 cysteine residues clustered near the N- and C-terminus. Accordingly, expression of the cloned IGFBP-3 cDNA in mammalian tissue culture cells results in secretion of the protein into the culture medium.IGFBP-3 shares high homology (33% amino acid identity) including conservation of all 18 cysteine residues with a smaller human IGF-binding protein (BP-28) identified in amniotic fluid. IGFBP-3 has one or more glycosylation sites with a protein core of ∼30 kDa. Western blots revealed that the 39-45 kDa IGFBP-3 fragment is a glycoprotein.
|