|
BP61907
|
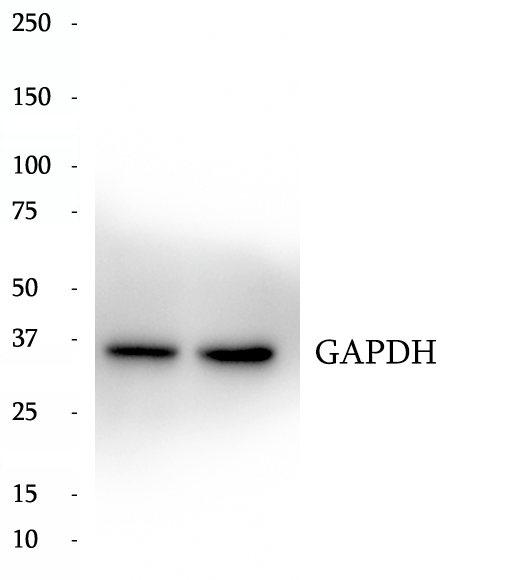
Anti-GGCX antibody
|
|
|
|
|
GGCX (Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase) is also named as GC and belongs to the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase family. This 94 kDa (including all modifications, such as the five N-linked glycosylations), is a 5-pass transmembrane protein and a key regulator of blood coagulation residues with the concomitant conversion of the reduced hydroquinone form of vitamin K to vitamin K epoxide. Defects in GGCX are a cause of combined deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors type 1 (VKCFD1) and pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like disorder with multiple coagulation factor deficiency (PXEL-MCFD).
|
|
BP60987
|
Anti-CLTB antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Clathrin is the major protein of the polyhedral coat of coated pits and vesicles which entrap specific macromolecules during receptor-mediated endocytosis. The clathrin molecule has a triskelion shape. Each clathrin triskelion is composed of three identical heavy chains (180 kDa) and three light chains of two types, LCA (CLTA) and LCB (CLTB) (30-40 kDa). The light chain subunits are thought to regulate the formation or disassembly of clathrin coats.
|
|
BP63631
|
Anti-Phospho-STAT1 (Ser727) antibody
|
|
|
|
|
STAT1 (signal transducers and activators of transcription 1) is a member of the STAT protein family. STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo-or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators.STAT1 activating phosphorylation at Ser727 is p38-dependant duringlipotoxic stress. MLK3 activation triggers a MAPK signaling cascade resulting in STAT1 Ser727 phosphorylation. The phosphorylation of STAT1 Ser727 increases its nuclear localization, and transcriptional activity..
|
|
BP60338
|
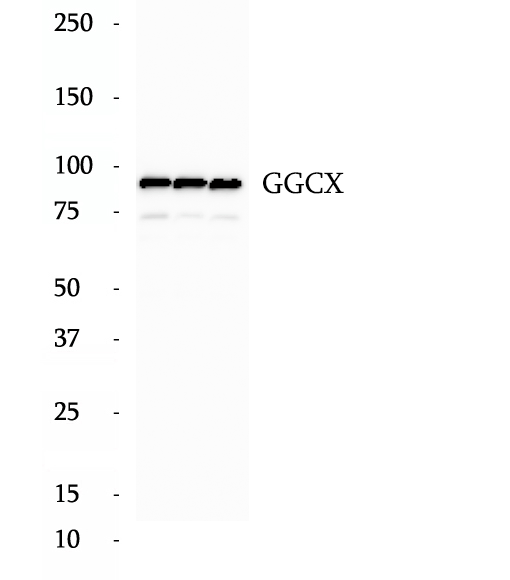
Anti-ASUN antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Asunder (ASUN) is a conserved protein that has been reported as a critical regulator of dynein localization during Drosophila spermatogenesis promotes dynein recruitment and centrosomal tethering to the nucleus at mitotic entry.
|
|
BP65270
|
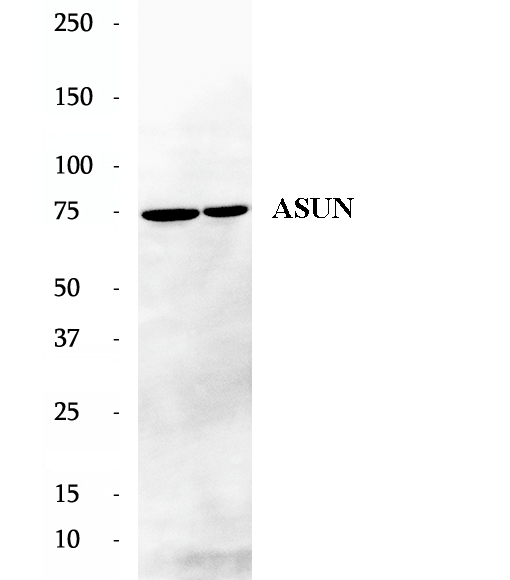
Anti-VPS54 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
VPS54 is a part of the Golgi-associated retrograde protein (GARP) complex protein required for tethering and fusion of endosome-derived transport vesicles to the trans-Golgi network. It may particpate in retrograde transport from early and late endosomes to the late Golgi. The GARP complex is required for the maintenance of the cycling of mannose 6-phosphate receptors between the TGN and endosomes, this cycling is necessary for proper lysosomal sorting of acid hydrolases such as CTSD.
|
|
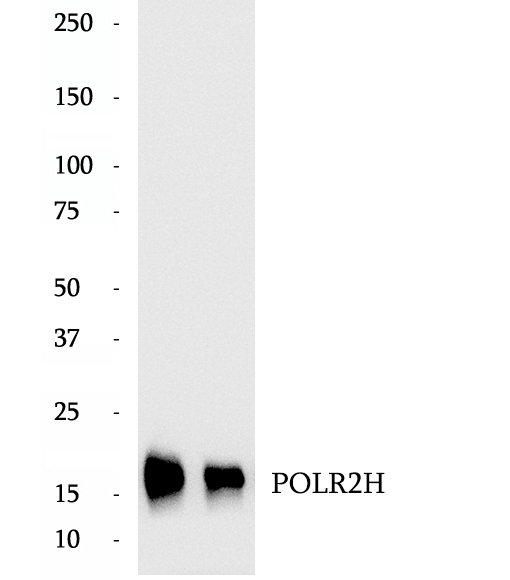
BP63756
|
Anti-POLR2H antibody
|
|
|
|
|
DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POLR2H gene. This gene encodes one of the essential subunits of RNA polymerase II that is shared by the other two eukaryotic DNA-directed RNA polymerases, I and III.
|
|
BP60591
|
Anti-C6orf130 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The function of C6orf130 remains largely unknown. Catalog#25249-AP is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against the full-length of human C6orf130. The MW of this protein is 17 kDa, and this antibody specially recognises the 17 kDa protein.
|
|
BP61795
|
Anti-FRS2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FRS2 gene. FRS2 is an 80 kDa membrane-anchored signal transducing adaptor protein that links specific activated Receptor Tyrosine Kinases to multiple downstream signaling pathways, most notably the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and PLCγ pathways. It is overexpressed and amplified in several cancer types, including prostate cancer.
|
|
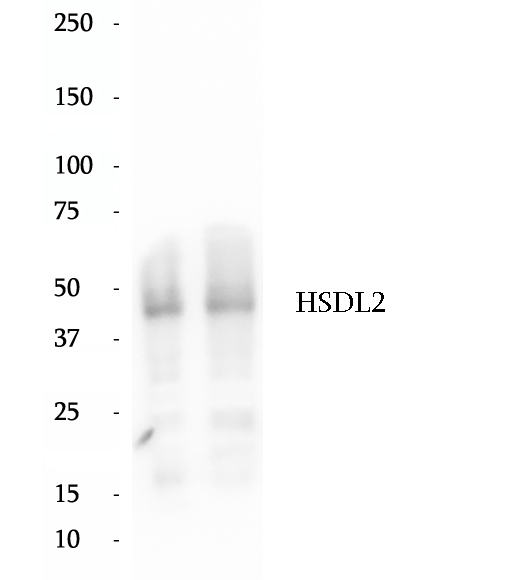
BP62239
|
Anti-HSDL2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Human hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like 2 (HSDL2) is a characterized SDR gene that not only catalyses the oxidation and reduction of multiple substrates but also regulates different metabolic and signalling pathways. Accumulating evidences suggest that HSDL2 play an important role in cancer progression. HSDL2 has promoting effects on tumor progression in papillary thyroid cancer, bladder cancer, ovarian cancer, and glioma, but has suppressing effects in cholangiocarcinoma. ( PMID: 31372054, PMID: 32211805)
|
|
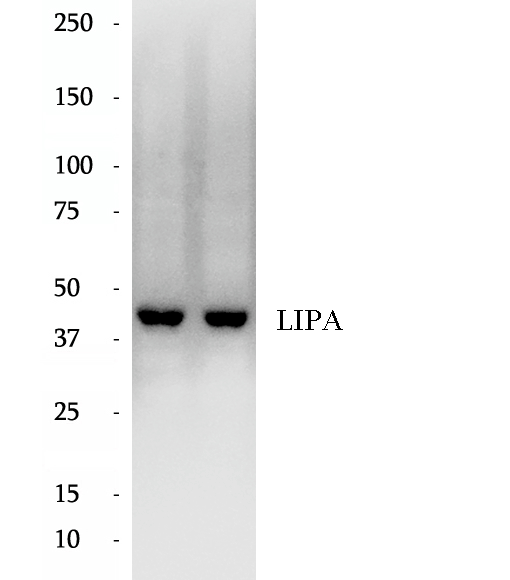
BP62629
|
Anti-LIPA antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Human acid lipase/cholesteryl esterase (LIPA) is a 46-kDa glycoprotein required for the lysosomal hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides that cells acquire through the receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoproteins and cholesteryl ester storage disease (CESD). It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 45 kDa and 39 kDa. The full length protein has a signal peptide and several glycosylation sites.
|
|
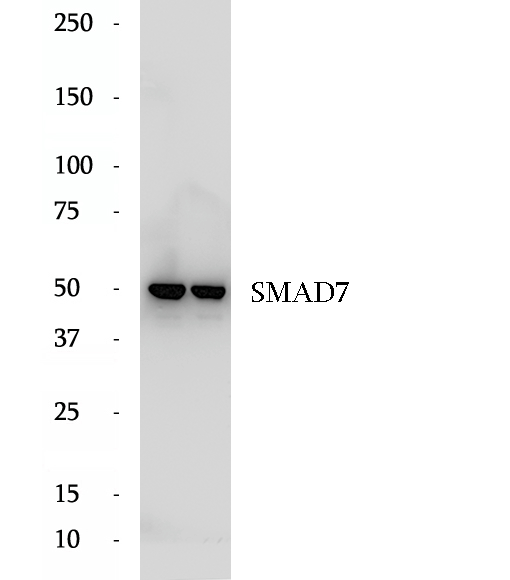
BP64487
|
Anti-SMAD7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SMAD7, also named as Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7, is a 426 amino acid protein, which belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family. SMAD7 Interaction with NEDD4L or RNF111 induces translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. TGF-beta stimulates its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. PDPK1 inhibits its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to TGF-beta. SMAD7 as antagonist of signaling by TGF-beta type 1 receptor superfamily members has been shown to inhibit TGF-beta and activin signaling by associating with their receptors thus preventing SMAD2 access. SMAD7 functions as an adapter to recruit SMURF2 to the TGF-beta receptor complex and also acts by recruiting the PPP1R15A-PP1 complex to TGFBR1, which promotes its dephosphorylation. SMAD7 positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator.
|
|
BP62464
|
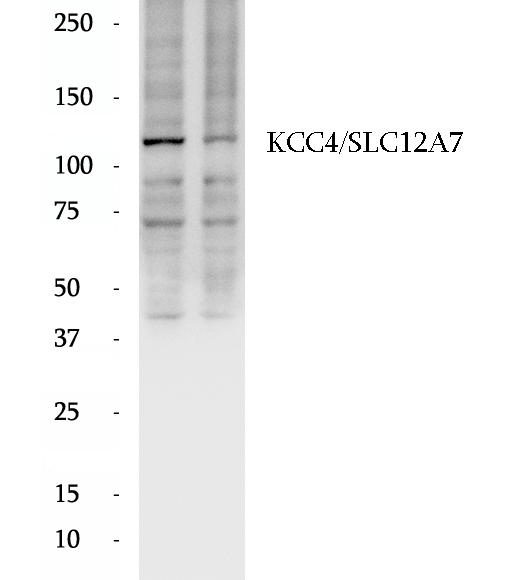
Anti-KCC4/SLC12A7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
KCC4, also named as Solute carrier family 12 member 7 (SLC12A7), is a 1083 amino-acid protein, which belongs to the SLC12A transporter family. As a multi-pass membrane protein, the molecular weight of KCC4 is 119 kDa. KCC4 mediates electroneutral potassium-chloride cotransport when activated by cell swelling. Moreover, KCC4 may mediate K+ uptake into Deiters' cells in the cochlea and contribute to K+ recycling in the inner ear. KCC4 is important for the survival of cochlear outer and inner hair cells and the maintenance of the organ of Corti (Uniprot, GeneID:10723).
|
|
BP64129
|
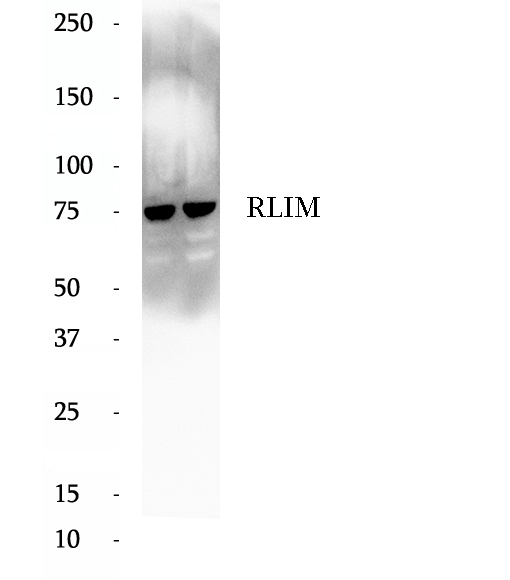
Anti-RLIM antibody
|
|
|
|
|
RLIM (RING finger LIM domain-binding protein), also known as RNF12 (RING finger protein 12) or NY-REN-43, is a 624 amino acid RING-H2 zinc finger protein that is involved in protein ubiquitinylation and subsequent degradation. Expressed in a variety of tissues, RLIM binds to the LIM domain of various proteins and functions as a protein ligase that negatively co-regulates LIM homeodomain (LIM-HD) transcription factors. Through its interaction with Sin3A, a component of the histone deacetylase corepressor complex, RLIM is able to recruit the corepressor complex to LIM-HD proteins, thereby inhibiting LIM-HD transcription. In addition to recruiting the deacetylase complex to LIM-HD proteins, RLIM is able to bind to, ubiquinate and subsequently degrade CLIM proteins, which function as positive co-regulators of LIM-HD transcription factors. RLIM contains one RING-type zinc finger and is implicated in renal cell carcinoma. The calcualted molecular weight of RLIM is 69 kDa, but modified RLIM is about 70-75 kDa.
|
|
BP62961
|
Anti-mTOR antibody
|
|
|
|
|
MTOR, also named as FRAP1, FRAP, FRAP2 and RAPT1, belongs to the PI3/PI4-kinase family.MTOR is a Ser/Thr protein kinase that functions as an ATP and amino acid sensor to balance nutrient availability and cell growth. MTOR is kinase subunit of both mTORC1 and mTORC2, which regulate cell growth and survival in response to nutrient and hormonal signals. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino-acids. mTORC2 is also activated by growth factors, but seems to be nutrient-insensitive. mTORC2 seems to function upstream of Rho GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton, probably by activating one or more Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors. mTORC2 promotes the serum-induced formation of stress-fibers or F-actin. MTOR has a calculated molecular mass of 289 kDa, and always can be detected at about 250 kDa due to some modifications.
|
|
BP62998
|
Anti-MYH4 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Myosin is one of the most important skeletal muscle proteins. MYH4 functions muscle contraction. The antibody is specific to MYH4.
|
|
BP69822
|
Goat Anti-mouse IgG (H+L), HRP-linked Antibody
|
|
|
|
|
This affinity purified goat anti-rabbit IgG (heavy and light chain) antibody is used in combination with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for chemiluminescence detection.
|
|
BP69823
|
Goat Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), HRP-linked Antibody
|
|
|
|
|
This affinity purified goat anti-Rabbit IgG (heavy and light chain) antibody is used in combination with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for chemiluminescence detection.
|
|
BP62594
|
Anti-LDHA antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is composed of A subunits predominate in skeletal muscle and B subunits are abundantly produced in brain and heart. The LDHA (lactate dehydrogenase A) and COPB1 (coatomer protein complex, subunit beta 1)genes, are involved in energy metabolism and protein transport processes. Both genes might play important roles in muscle development. It has some isoforms with the molecular mass of 27-40 kDa and can form a homotetramer.
|
|
BP60614
|
Anti-CACNA1S antibody
|
|
|
|
|
CACNA1S, also named as CACH1, CACN1 and CACNL1A3, belongs to the calcium channel alpha-1 subunit (TC 1.A.1.11) family and CACNA1S subfamily. Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. CACNA1S gives rise to L-type calcium currents. Long-lasting (L-type) calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group. The antibody is specific to CACNA1S.
|
|
BP61088
|
Anti-CRABP1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins including CRABP1 and CRABP2 bind retinoic acid (RA), an important regulator of cell growth and differentiation, thus play an important role in RA-mediated differentiation and proliferation processes. It has been reported that CRABP1 influences the biological effects of RA in cell-selective manners by enhancing the physiological function of RA in keratinocytes or inhibiting RA-induced differentiation of neuroblastoma cells.
|

 antibody.gif)




, HRP-linked Antibody.gif)