|
BP62332
|
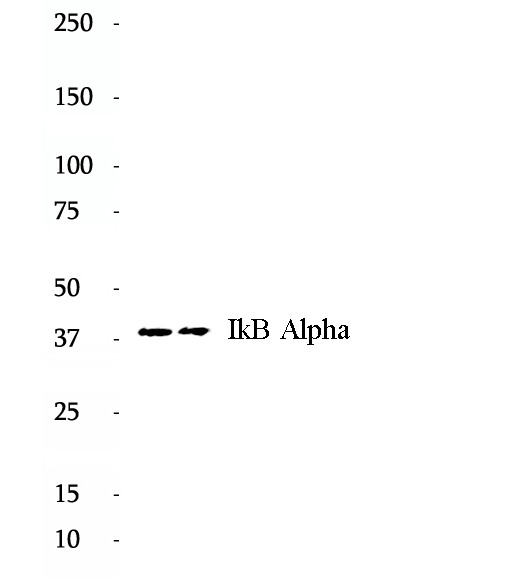
Anti-IkB Alpha antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (NFKBIA, synonyms: IKBA, MAD-3, NFKBI).NFKB1 or NFKB2 is bound to REL, RELA, or RELB to form the NFKB complex. The NFKB complex is inhibited by I-kappa-B proteins (NFKBIA or NFKBIB), which inactivate NF-kappa-B by trapping it in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of serine residues on the I-kappa-B proteins by kinases (IKBKA, or IKBKB) marks them for destruction via the ubiquitination pathway, thereby allowing activation of the NF-kappa-B complex. Activated NFKB complex translocates into the nucleus and binds DNA at kappa-B-binding motifs such as 5-prime GGGRNNYYCC 3-prime or 5-prime HGGARNYYCC 3-prime.
|
|
BP61487
|
Anti-EIF1AX antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-chromosome (EIF1AX), designated as to distinguish from the Y-linked homolog, has an unblocked N-terminal proline, which was consistent with the general pattern of eukaryotic protein. It's may be required for maximal rate of protein biosynthesis. Like EIF4C, it enhances ribosome dissociation into subunits and stabilizeds the binding of the initiator Met-tRNA (l) to 40S ribosomal subunits.
|
|
BP61822
|
Anti-GABARAPL1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
GABARAPL1 (GABARAP-like protein 1), also named as ATG8, GEC1, APG8L, ATG8L and APG8-LIKE, is a member of GABARP (GABAA receptor-associated protein) family. GABARAPL1 was initially identified as estrogen-regulated gene and the protein acts in receptor and vesicle transport. It's also involved in the process of autophagy like GABARAP and GABARAPL2, and may be considered as an autophagic marker. It is expressed at very high levels in the brain, heart, peripheral blood leukocytes, liver, kidney, placenta and skeletal muscle and at very low levels in thymus and small intestine. The antibody is specific to GABARAPL1, and it doesn't recognize the recombinant GABARAP and GABARAPL2.
|
|
BP61936
|
Anti-GLRX2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
GLRX2 (Glutaredoxin-2) is also named as GRX2 and belongs to the glutaredoxin family. It facilitates the maintenance of cellular redox homeostasis upon treatment with apoptotic agents, thereby preventing cardiolipin oxidation and cytochrome C release. The GLRX2, which exists in a dynamic equilibrium of enzymatically active monomers and quiescent dimers,is a 16-kDa protein directed either to the nucleus or to the mitochondria through differential splicing of the first exon. It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.
|
|
BP63379
|
Anti-PAEP/Glycodelin antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Glycodelin (also known as Progestagen Associated Endometrial Protein, PAEP, and Placental Protein 14, PP14) is a secreted human lipocalin-family protein mainly expressed in well-differentiated epithelial cells in human reproductive tissues, like endometrium and seminal vesicles. While different cells produce differentially glycosylated isoforms of Glycodelin: decidualized endometrium-derived glycodelin-A (GdA), seminal vesicle-derived glycodelin-S (GdS), glycodelin-F (isolated from follicular fluid), and glycodelin-C (isolated from cumulus cells). Glycodelin has been involved in cell differentiation and tumor growth.
|
|
BP63448
|
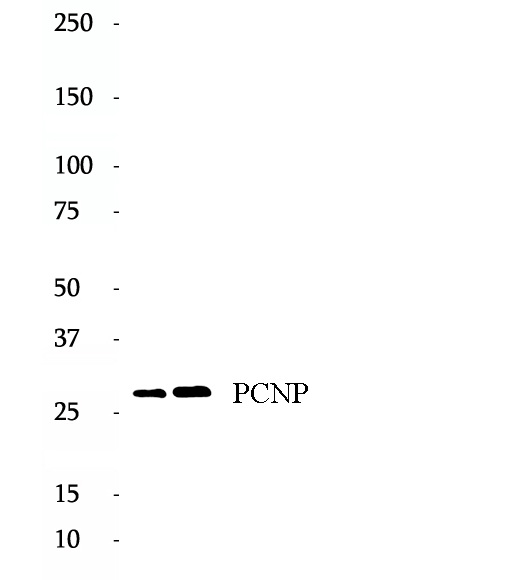
Anti-PCNP antibody
|
|
|
|
|
PEST-containing nuclear protein (PCNP), a novel nuclear protein, is involved in vital cellular processes like cell proliferation and mediates tumorigenesis. PCNP is a short-living, small nuclear protein of only 178 amino acids with two remarkable PEST sequences that are rich in proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T). The current understanding of PCNP reveals that PCNP has the ability to interact with cell cycle regulatory proteins; tumor suppressors (p53 and pRB), and promoters (cyclin E and cyclin D) to determine the fate of tissues to facilitate the process of either apoptosis or cell proliferation.
|
|
BP64384
|
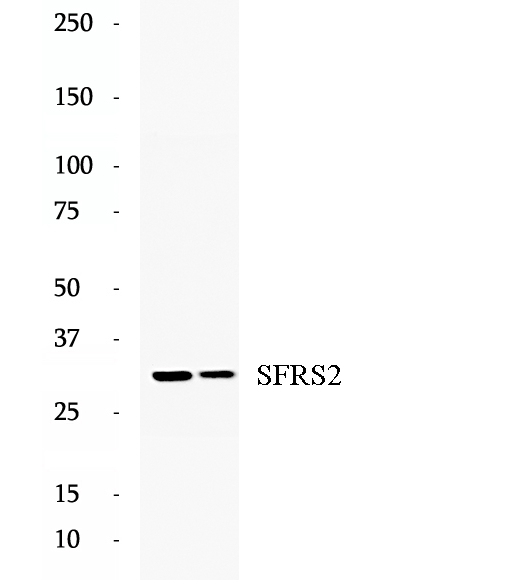
Anti-SFRS2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SFRS2, also named as PR264 and Splicing component, 35 kDa, belongs to the splicing factor SR family. SFRS2 is necessary for the splicing of pre-mRNA. Some residue of SFRS2 is modified by phosphorylase and acetylase after translation. The molecular weight of modified SFRS2 is 35-40kDa. It is required for formation of the earliest ATP-dependent splicing complex and interacts with spliceosomal components bound to both the 5'- and 3'-splice sites during spliceosome assembly. It also is required for ATP-dependent interactions of both U1 and U2 snRNPs with pre-mRNA. It binds to purine-rich RNA sequences, either 5'-AGSAGAGTA-3' (S=C or G) or 5'-GTTCGAGTA-3'. SFRS2 can bind to beta-globin mRNA and commit it to the splicing pathway. The antibody has no cross reaction to SFRS2B.
|
|
BP64546
|
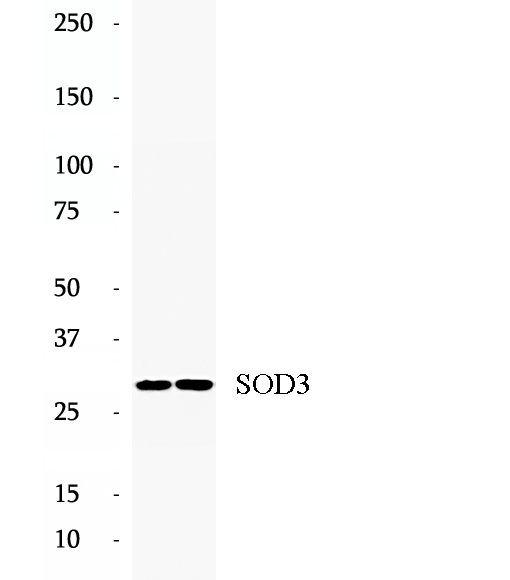
Anti-SOD3 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
SOD is located intracellular (SOD-1; cytosolic, SOD-2; mitochondrial matrix) and extracellular (SOD-3), and catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide anion to H2O2.SOD3, or EC-SOD, is the most recently characterized SOD, exists as a copper and zinc-containing tetramer, and is synthesized containing a signal peptide that directs this enzyme exclusively to extracellular spaces. SOD-3 is a Mn-containing tetrameric protein with a subunit Mr of 24-35 kDa. The activity of EC-SOD is dependent on its ability to form a tetramer of 135 kDa.
|
|
BP64411
|
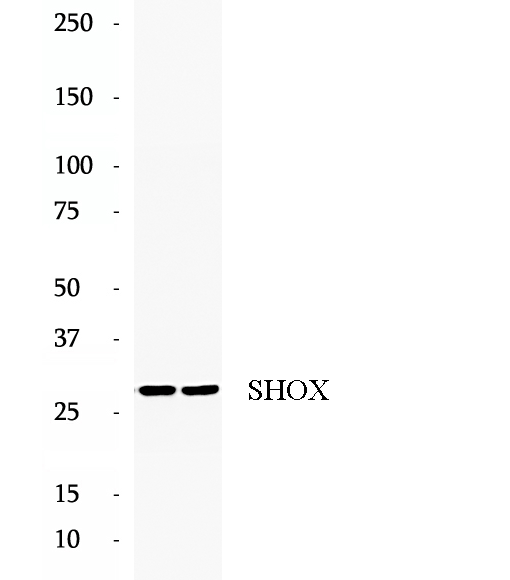
Anti-SHOX antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Short stature homeobox protein (SHOX), also named as GCFX, is a 292 amino acid protein, which contains one homeobox DNA-binding domain and belongs to the paired homeobox family. SHOX. SHOX controls fundamental aspects of growth and development. SHOX undergoes splicing resulting in two isoforms, SHOXA and SHOXB. SHOXA is a 32 kDa protein and is expressed in skeletal muscle, placental, pancreas, heart and bone marrow fibroblast and, to a lesser extent, in kidney and lung. SHOXB is 25 kDa protein and is highly expressed in osteogenic cells, but not expressed in brain, kidney, liver or lung.
|
|
BP64525
|
Anti-SNRPB2 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein B'' (SNRPB2) is part of the U2 RNP particle, which associated with the branch point of the lariat-shaped intron, in intermediate in the cascade of mRNA precursor splicing event. Only in presence of the U2A' protein, SNRPB2 binds stem loop IV of U2 snRNA.
|
|
BP63174
|
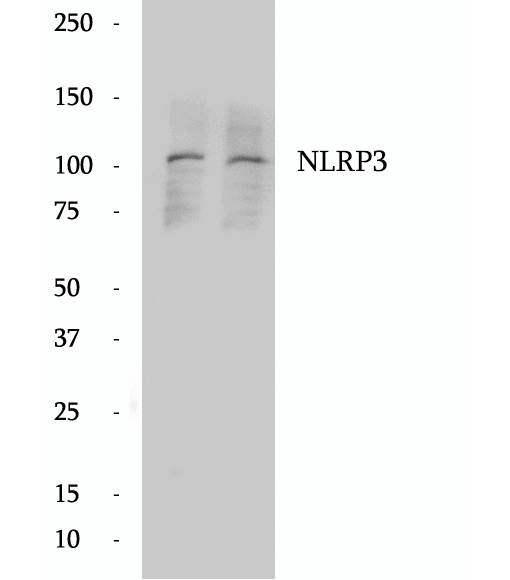
Anti-NLRP3 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
NLRP3, also named as C1orf7, CIAS1 and PYPAF1, belongs to the NLRP family. NLRP3 may function as an inducer of apoptosis. It interacts selectively with ASC and this complex may function as an upstream activator of NF-kappa-B signaling. NLRP3 inhibits TNF-alpha induced activation and nuclear translocation of RELA/NF-KB p65. Also inhibits transcriptional activity of RELA. NLRP3 activates caspase-1 in response to a number of triggers including bacterial or viral infection which leads to processing and release of IL1B and IL18. Defects in NLRP3 are the cause of familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome type 1 (FCAS1) which also known as familial cold urticaria. Defects in NLRP3 are a cause of Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS) which is urticaria-deafness-amyloidosis syndrome. Defects in NLRP3 are the cause of chronic infantile neurologic cutaneous and articular syndrome (CINCA) which also known as neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID). The antibody recognizes the C-term of NLRP3.
|
|
BP62340
|
Anti-IL-1 beta antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Interleukin-1, produced mainly by blood monocytes, mediates the panoply of host reactions collectively known as acute phase response. It is identical to endogenous pyrogen. The multiple biologic activities that define IL1 are properties of a 15- to 18-kD protein that is derived from a 30- to 35-kD precursor. Interleukin 1β (IL-1B) is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. It is a pro-inflammatory cytokine against infection, playing an important role in the pathogenesis of cancers. It signals through various adaptor proteins and kinases that lead to activation of numerous downstream targets.
|
|
BP62279
|
Anti-Goat IBA1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA1), also known as Allograft inflammatory factor-1 (AIF-1), is an inflammation-responsive scaffold protein expressed and secreted from macrophages. Microglia response factor (MRF-1) and daintain are also similar, and likely identical, proteins. IBA1 is necessary for macrophage survival, and it is also a key molecule in proinflammatory activity. IBA1 is a cytoplasmic protein, often expressed in immunocytes, macrophages, and microglia. It can be used as a marker for normal microglia in brain tissue, as IBA1 is expressed by all microglial cell subpopulations.
|
|
BP61173
|
Anti-CXCR7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
CXCR7 (C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7), also known as RDC1, is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor family. CXCR7 can bind the chemokines CXCL11 and CXCL12 with high affinity, and it also acts as coreceptor with CXCR4 for a restricted number of HIV isolates. Expression of CXCR7 has been associated with cardiac development as well as with tumor growth and progression. This antibody recognizes endogenous CXCR7, which has an experimentally determined molecular weight of 50 kDa.
|
|
BP60829
|
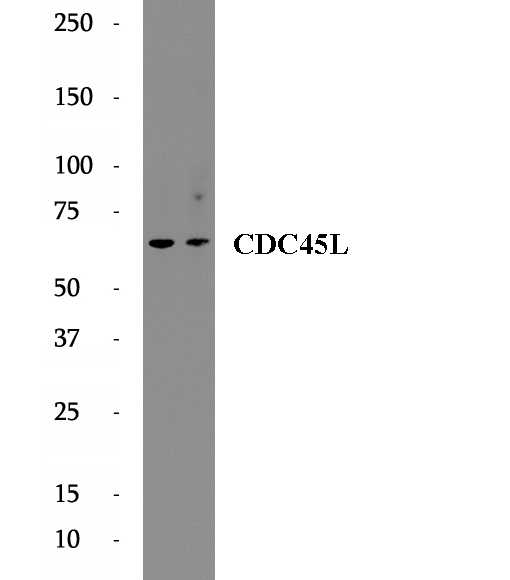
Anti-CDC45L antibody
|
|
|
|
|
CDC45L (Cell division control protein 45 homolog), plays a role in the initiation of DNA replication, and genetically interacts with MCM family members and with ORC2 and physically form a complex including Mcm5p. It's the first gene missed in DiGeorge syndrome that suggest involve in cell proliferation. This is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against part of C-terminus of human CDC45L.
|
|
BP61826
|
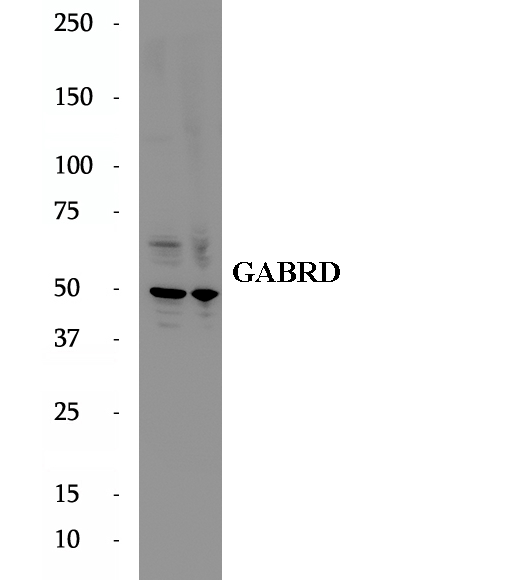
Anti-GABRD antibody
|
|
|
|
|
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain, The GABRD gene encodes the delta subunit of the ligand-gated chloride channel for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
|
|
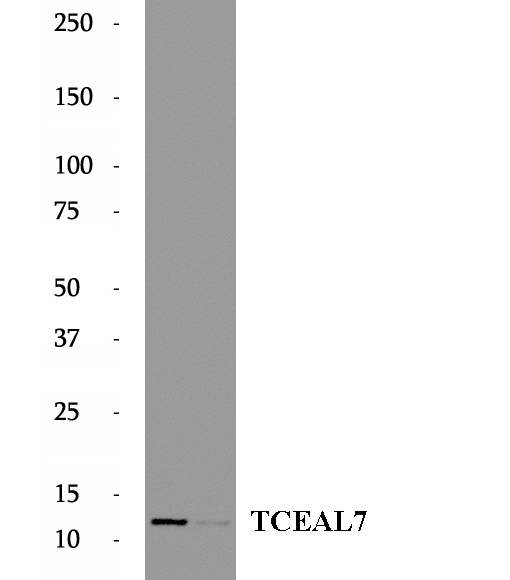
BP64789
|
Anti-TCEAL7 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
TCEAL7 is a transcription regulatory factor that has a role in the negative regulation of NF-kappa-B signaling at the basal level by regulating transcriptional activity of NF-kappa-B on its target gene promoters. It can associate with cyclin D1 promoter containing Myc E-box sequence and transcriptionally represses cyclin D1 expression. In addition, TCEAL7 regulates telomerase reverse transcriptase expression and telomerase activity in both ALT (alternative lengthening of telomeres)and telomerase-positive cell lines
|
|
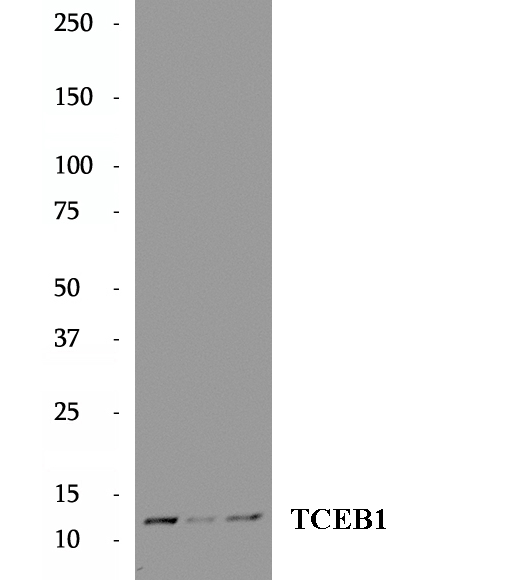
BP64790
|
Anti-TCEB1 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
TCEB1, also named as RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII subunit C, belongs to the SKP1 family. It mediates the ubiquitination of ECS-E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes. TCEB1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer cell line PC-3 and breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3. TCEB1 also promotes invasion of prostate cancer cells.
|
|
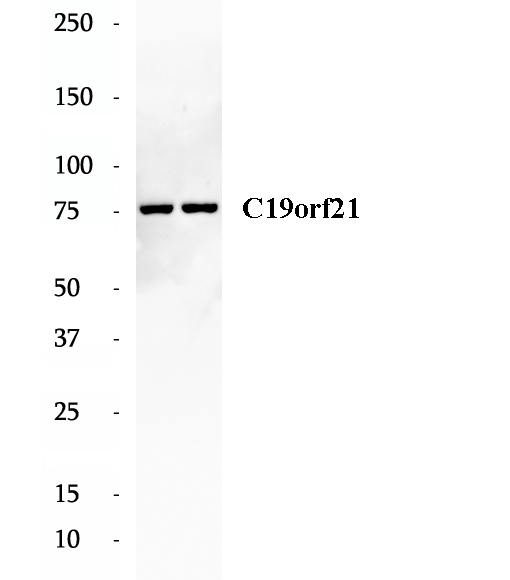
BP60557
|
Anti-C19orf21 antibody
|
|
|
|
|
C19orf21, also named as MISP, plays a role in mitotic spindle orientation and mitotic progression. It may be required for directed cell migration and centrosome orientation. C19orf21 regulates the distribution of dynactin at the cell cortex in a PLK1-dependent manner.
|
|
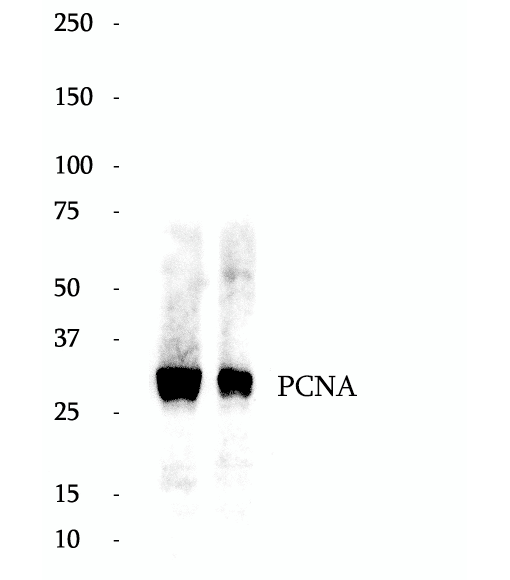
BP69337
|
HRP Anti-PCNA antibody
|
|
|
|
|
The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a protein synthesized in early G1 and S phases of the cell cycle, functions in cell cycle progression, DNA replication and DNA repair. In early S phase, PCNA exhibits granular distribution and is absent from the nucleoli; however, in late S phase, it relocates to the nucleoli. PCNA exists in two basic forms: one involved in ongoing DNA replication, which localizes specifically to the nucleus, and a second, soluble form, not implicated in constant synthesis. Interestingly, the latter form degrades in the presence of organic solvents, rendering it undetectable by histological methods in tissues using organic fixatives, and thus also providing a method of visualizing only the synthesizing form.This antibody specifically react with the 36kd human PCNA protein.
|