|
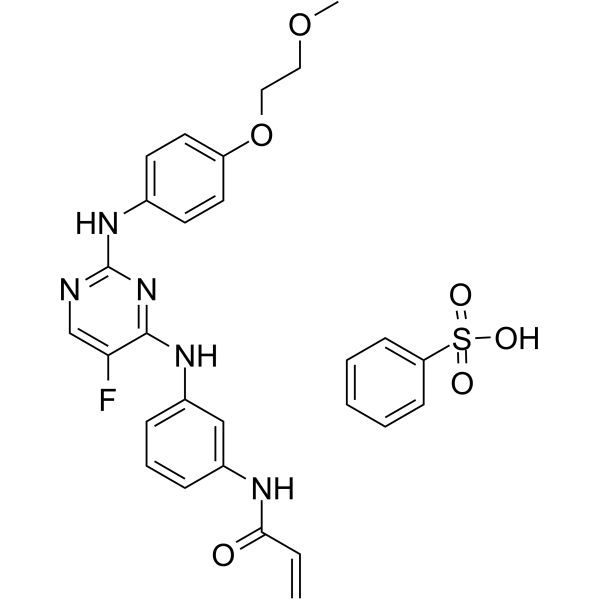
BP10417
|
Spebrutinib besylate
|
|
|
|
|
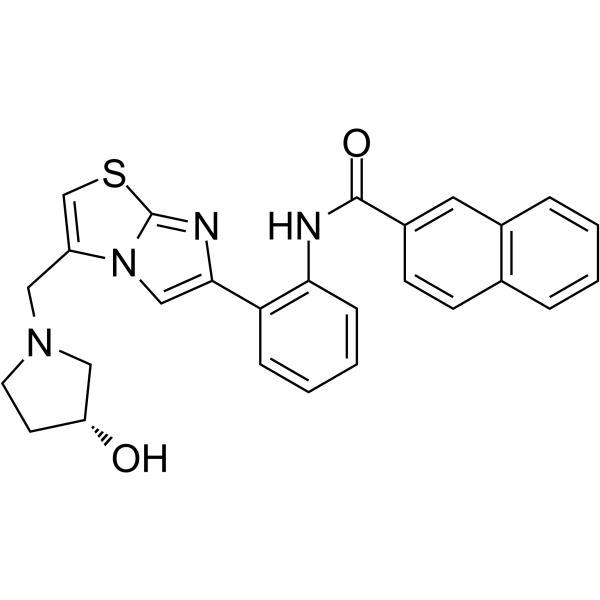
Spebrutinib besylate (AVL-292 benzenesulfonate; CC-292 besylate) is a Btk kinase activity inhibitor (IC50<0.5 nM, Kinact/Ki=7.69×104 M-1s-1s).
|
|
BP10413
|
SPP-86
|
|
|
|
|
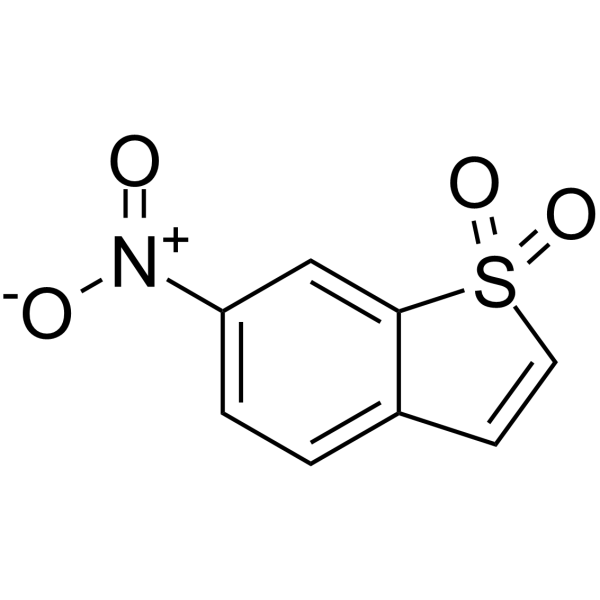
SPP-86 is an effective and selective cell-permeable inhibitor of RET tyrosine kinase with an IC50 of 8 nM.
|
|
BP10988
|
squarunkinA
|
|
|
|
|
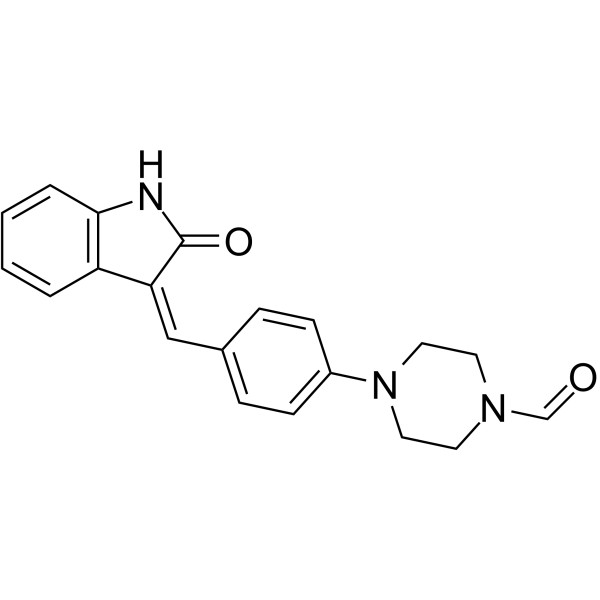
squarunkinA is a novel modulator of the UNC119-Cargo Interaction, potently and selectively inhibiting the binding of a myristoylated peptide representing the N-terminus of Src kinase to UNC119A
|
|
BP10781
|
Src Inhibitor 1
|
|
|
|
|
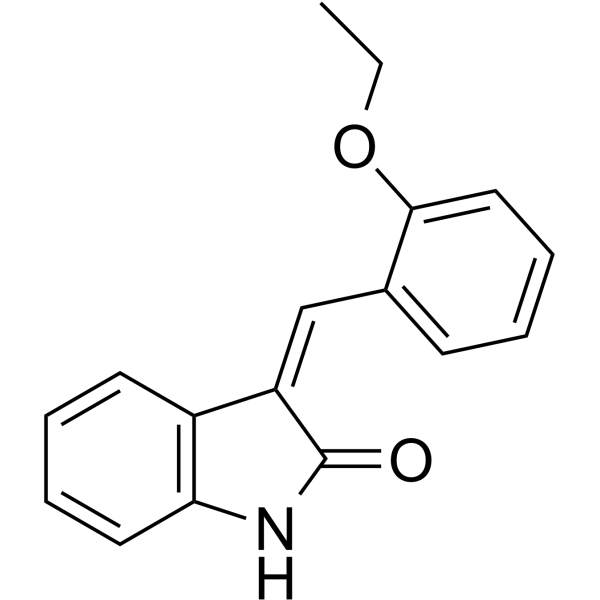
Src Inhibitor 1 is a potent and selective dual site Src tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
|
|
BP10574
|
SRS11-92
|
|
|
|
|
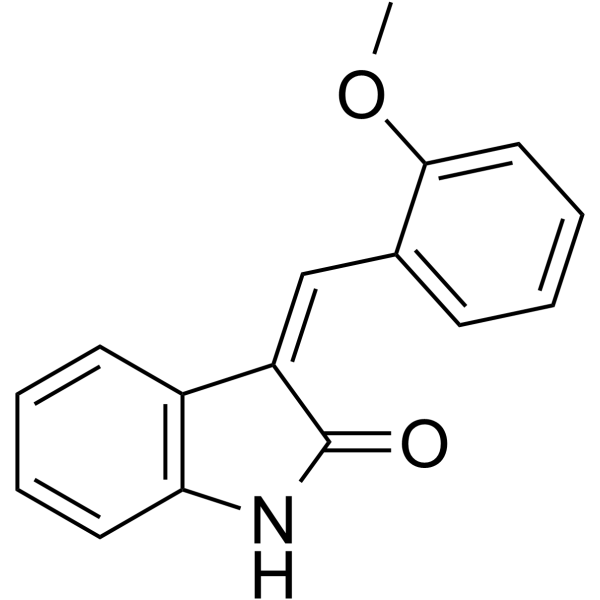
SRS11-92 is a ferroptosis inhibitor and a derivative of ferrostatin-1
|
|
BP10783
|
SRS16-86
|
|
|
|
|
SRS16-86 is a novel third-generation ferrostatin, is an inhibitor of ferroptosis.
|
|
BP10005
|
SRT 2183
|
|
|
|
|
SRT 2183 (1-10 μM; 24-72 hours) inhibits the growth of Reh and Nalm-6 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. SRT 2183 (5-10 μM in Reh cells; 10 μM in Ly3 cells; 24 hours) induces expression of DNA-damage response genes associated with accumulation of phospho-H2A.X levels. SRT2183 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation, fusion and resorptive capacity without affecting osteoclast survival.
|
|
BP10430
|
SSE15206
|
|
|
|
|
SSE15206 is a microtubule polymerization inhibitor that overcomes multidrug resistance. Causes aberrant mitosis resulting in G2/M arrest due to incomplete spindle formation in cancer cells.
|
|
BP10017
|
Stachyose tetrahydrate
|
|
|
|
|
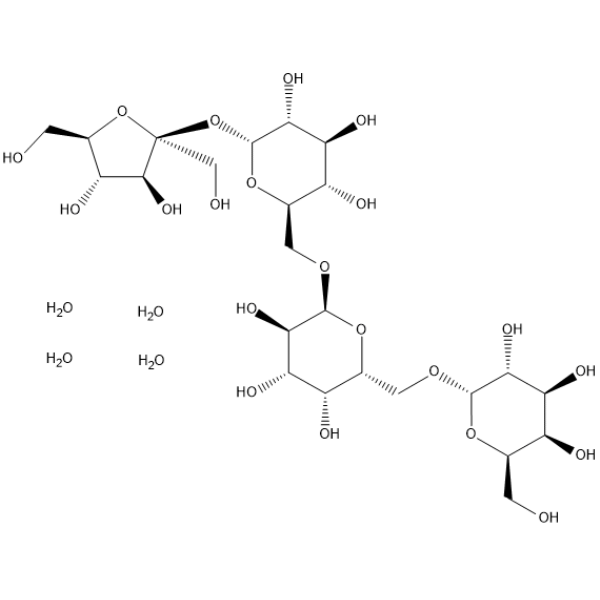
Stachyose is a tetrasaccharide consisting of two α-D-galactose units, one α-D-glucose unit, and one β-D-fructose unit sequentially.
|
|
BP10952
|
STAT3-IN-1
|
|
|
|
|
STAT3-IN-1 selective and orally active inhibitor of STAT3(in HT29 and MDA-MB 231 cells, with IC50 values of 1.82 μM and 2.14 μM , respectively), induces tumor apoptosis.
|
|
BP10922
|
Stattic
|
|
|
|
|
Stattic is a small molecule inhibitor of STAT3. It selectively inhibits STAT3 activation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation (IC50: 5.1 μM).
|
|
BP10847
|
SU 4981
|
|
|
|
|
SU 4981 is an inhibitor of VEGFR and a modulator of tyrosine kinase activity.
|
|
BP10736
|
Su1498
|
|
|
|
|
SU 1498 is a selective inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinase VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2, aka FLK1; IC50 = 700 nM), having negligible activity at several other serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases.1, 2 It effectively blocks signaling through VEGFR2 both in vitro and in vivo.1, 3 SU 1498 is used to study the role of VEGFR2 signaling in diverse processes, including angiogenesis, tumor growth, neural progenitor cell survival, and neuroregeneration.
|
|
BP10848
|
SU4984
|
|
|
|
|
SU4984 is a cell-permeable, ATP-competitive and reversible inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1).
|
|
BP10850
|
SU5204
|
|
|
|
|
SU5204, an analogue of SU5025, pharmacologically inhibits VEGFR2(IC50s of 4 and 51.5 μM for FLK-1 (VEGFR-2) and HER2)
|
|
BP10849
|
SU5214
|
|
|
|
|
SU 5214 is a modulator of tyrosine kinase signal transduction.
|
|
BP10662
|
SU5408
|
|
|
|
|
VEGFR2 Kinase Inhibitor I is a potent, cell-permeable inhibitor of the VEGFR2 kinase.
|
|
BP10815
|
Sulfatinib
|
|
|
|
|
Sulfatinib may be a potent drug for cancer. It inhibits KDR and FGFR1 enzymatic activity. It also is a hERG inhibitor.
|
|
BP10156
|
Sunitinib-d10
|
|
|
|
|
Sunitinib D10 is a deuterium labeled Sunitinib. Sunitinib is a inhibitor of multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase(IC50s of 80 nM and 2 nM for VEGFR2 and PDGFRβ, respectively).
|
|
BP10344
|
Suramin Sodium Salt
|
|
|
|
|
Suramin Sodium is a sodium salt form of suramin, a polysulphonated naphthylurea with potential antineoplastic activity. Suramin blocks the binding of various growth factors, including insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), epidermal growth factor (EGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and tumor growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), to their receptors, thereby inhibiting endothelial cell proliferation and migration. This agent also inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)- and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-induced angiogenesis; retroviral reverse transcriptase; uncoupling of G-proteins from receptors; topoisomerases; cellular folate transport; and steroidogenesis.
|