|
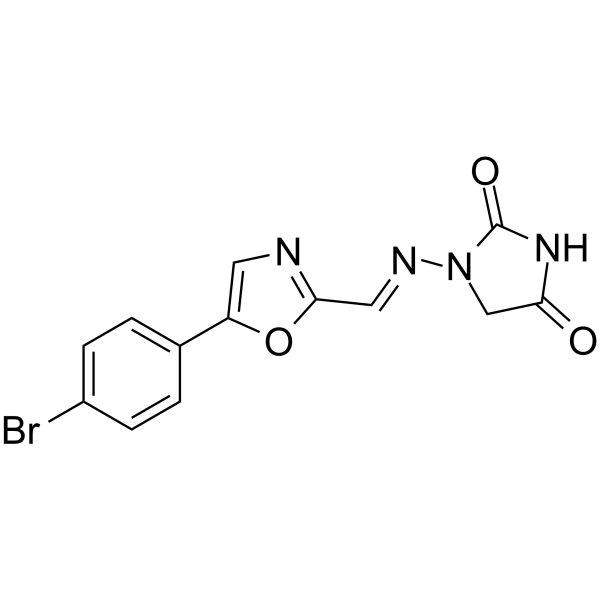
BP15921
|
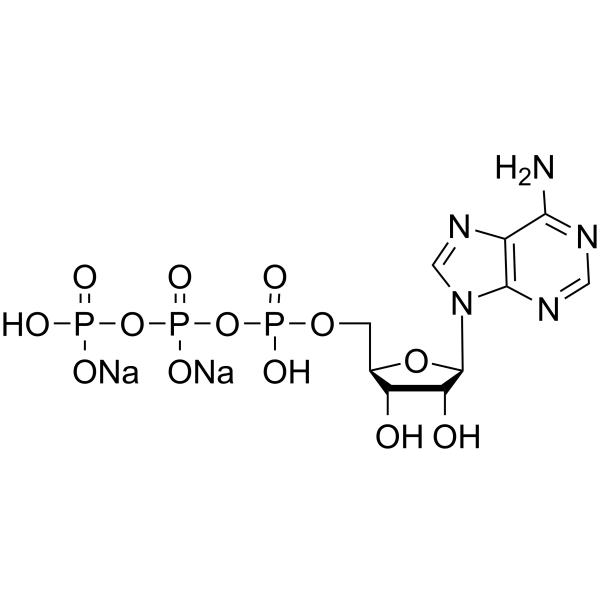
ATP disodium salt
|
|
|
|
|
Adenosine 5'-triphosphate disodium salt is a P2 purinoceptor agonist.
|
|
BP15922
|
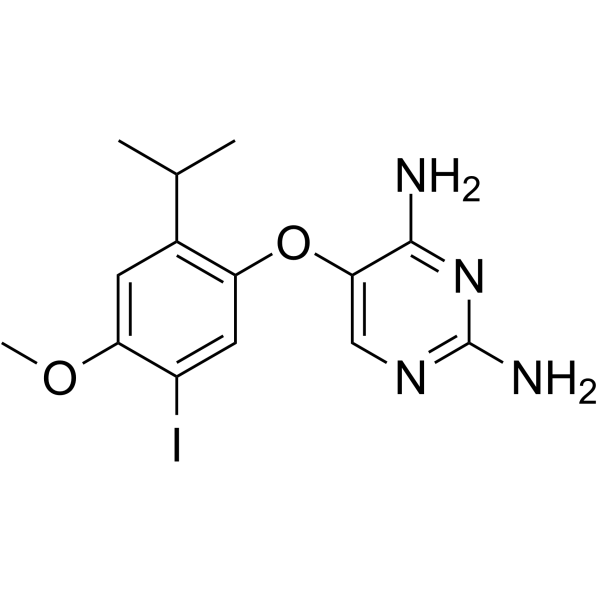
AF-353
|
|
|
|
|
AF-353, an effective and orally bioavailable antagonist of the P2X3/P2X2/3 receptor, inhibits human and rat P2X3 (pIC50= 8.0).
|
|
BP15923
|
Aflatrem
|
|
|
|
|
Aflatrem is a tremorgenic mycotoxin with acute neurotoxic effects, a single low dose of aflatrem is able to induce degeneration of neuronal processes in hippocampal neurotransmitter systems. Aflatrem potentiates the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced chloride current, the potentiating action of aflatrem on the GABAA receptor channel may explain the initial symptoms of intoxication caused by aflatrem in vivo.
|
|
BP15924
|
Afoxolaner
|
|
|
|
|
Afoxolaner is an isoxazoline insecticide/acaricide against Ixodes scapularis in dogs. Afoxolaner acts on the insect GABA and glutamate receptors, inhibiting GABA & glutamate-regulated uptake of chloride ions, resulting in excess neuronal stimulation and death of the arthropod.
|
|
BP15925
|
Alismol
|
|
|
|
|
Alismol has antihypertensive action, it decreases cardiac output, heart rate and left ventricular pressure, but it increases coronary flow, it has been used for the prevention of anginal attacks.
|
|
BP15926
|
Alisol F 24-acetate
|
|
|
|
|
Alisol F 24-acetate is a natural product isolated from Alisma plantago-aquatica Linn. Alisol F 24 Acetate enhances chemosensitivity and apoptosis of MCF-7/DOX Cells by inhibiting P-Glycoprotein-Mediated drug efflux.
|
|
BP15927
|
Almitrine mesylate
|
|
|
|
|
Almitrine dimesylate inhibits selectively the Ca2+-dependent K+ channel and that in rat chemoreceptor cells,used in the treatment of hypoxemic chronic lung diseases.
|
|
BP15928
|
alpha-Asarone
|
|
|
|
|
Alpha-Asarone is a psychoactive compound with antidepressant-like activity in mice.
|
|
BP15929
|
Alpidem
|
|
|
|
|
Alpidem is an anxiolytic drug from the imidazopyridine family. Alpidem does not produce sedative effects at normal doses, and is instead used specifically for the treatment of anxiety. Alpidem has nanomolar binding affinity for both the central benzodiaze
|
|
BP15930
|
AMG2850
|
|
|
|
|
AMG2850 is a potent, orally bioavailable, and selective antagonist of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8).
|
|
BP15931
|
Amlodipine Besylate
|
|
|
|
|
Amlodipine Besylate is a long-lasting calcium channel blocker.
|
|
BP15932
|
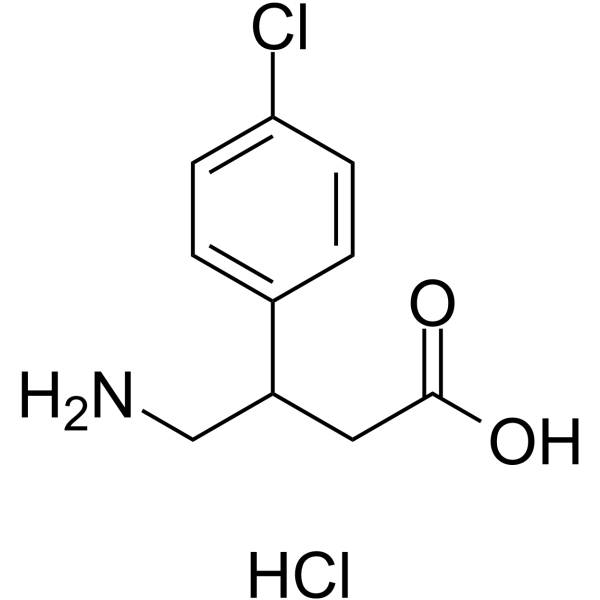
(R)-Baclofen hydrochloride
|
|
|
|
|
Arbaclofen hydrochloride, a Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid derivative, is a specific agonist of GABA-B receptors, it is used to treat spasticity, especially that due to spinal cord damage. It acts at spinal and supraspinal sites, generally reduces excitatory transmission.
|
|
BP15933
|
Asebogenin
|
|
|
|
|
Asebogenin has anti-bacterial activity, it shows inhibitory activity against S. aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (IC50 of 10 and 4.5 micrograms/ml, respectively); it shows antiplasmodial activities against both a chloroquine-sensitive and a resistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum. Asebogenin can inhibit the proliferation of murine B cells.
|
|
BP15934
|
ASP7663
|
|
|
|
|
ASP7663 is a TRPA1 Receptor Agonist and exhibiting an abdominal analgesic effect in vivo.
|
|
BP15935
|
ATP synthase inhibitor 1
|
|
|
|
|
ATP synthase inhibitor 1 is an inhibitor of the c subunit of the F1/FO-ATP synthase complex. It inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening and does not affect ATP levels.
|
|
BP15936
|
Atpenin A5
|
|
|
|
|
Atpenin A5 is a potent and highly specific complex II inhibitor (IC50 ~10 nM). Atpenin A5 is also an effective mKATP channel agonist and cardioprotective agent.
|
|
BP15937
|
AVE-0118
|
|
|
|
|
AVE-0118 is a potassium channel blocker and suppresses persistent atrial fibrillation.
|
|
BP15938
|
AZD9056 hydrochloride
|
|
|
|
|
AZD9056 hydrochloride is a P2X7 inhibitor,Which plays a significant role in pain-causing diseases and inflammation.
|
|
BP15939
|
Azumolene
|
|
|
|
|
Azumolene
|
|
BP15940
|
Baclofen hydrochloride
|
|
|
|
|
Baclofen hydrochloride is a GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID derivative that is a specific GABA-B RECEPTORS agonist. It is used in the treatment of MUSCLE SPASTICITY, especially that due to SPINAL CORD INJURIES. Its therapeutic effects result from actions at spinal and supraspinal sites, generally the reduction of excitatory transmission.
|

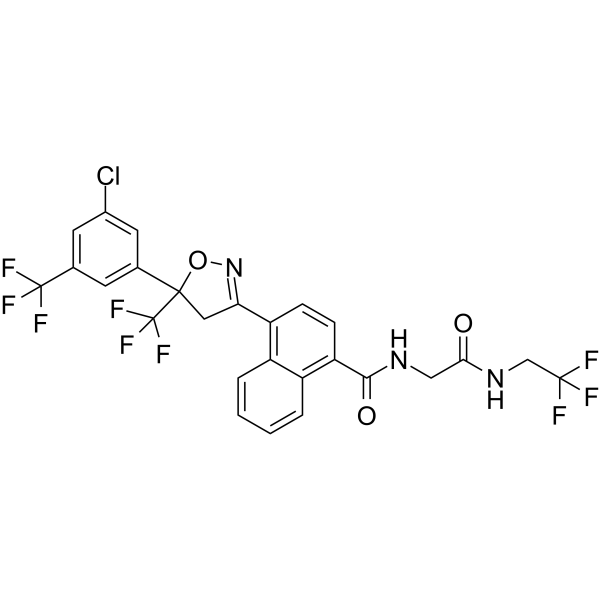


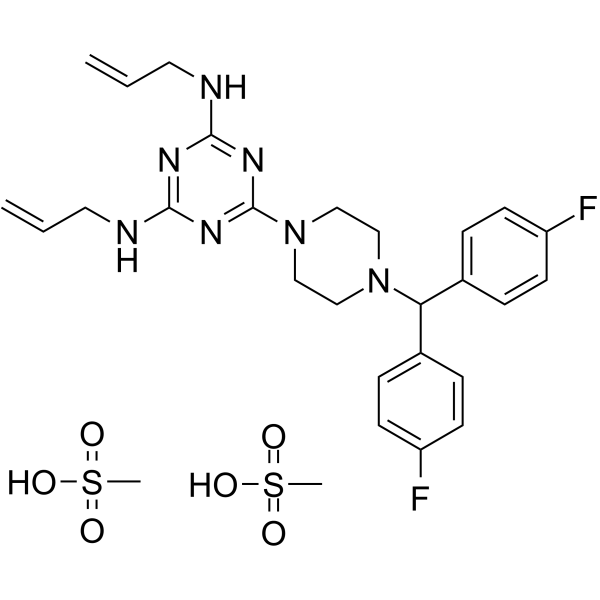
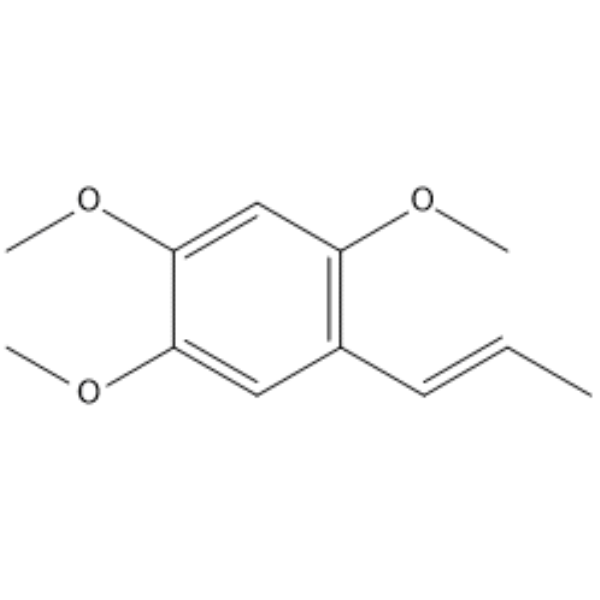
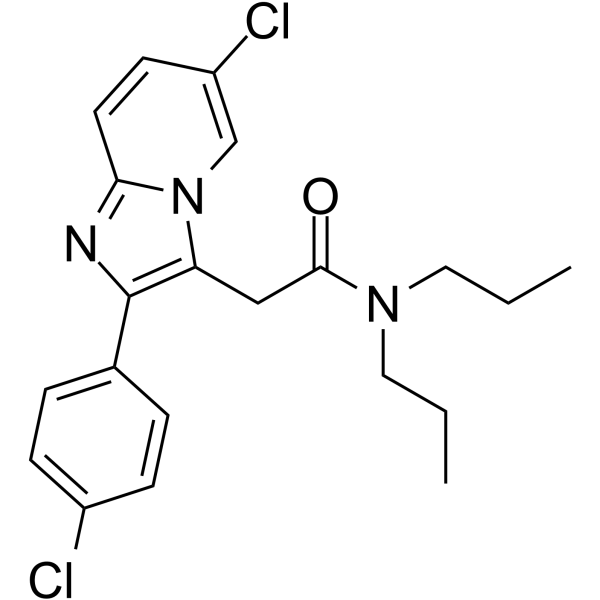

-Baclofen hydrochloride.gif)